Surgical Outcomes of Sigmoid Sinus Resurfacing for Pulsatile Tinnitus: The Predictive Value of the Water Occlusion Test and Imaging Studies
- PMID: 37475140
- PMCID: PMC10471903
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2023.00388
Surgical Outcomes of Sigmoid Sinus Resurfacing for Pulsatile Tinnitus: The Predictive Value of the Water Occlusion Test and Imaging Studies
Abstract
Objectives: Sigmoid sinus resurfacing (SS-R) is one of the most effective surgical treatments for patients with pulsatile tinnitus (PT) originating from anatomical variants of the vascular walls in the temporal bone. This study aimed to provide updated information on the clinical outcomes of SS-R and evaluate the efficacy of the water occlusion test (WOT) as an additional diagnostic modality.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed medical records including tinnitus questionnaires, temporal bone computed tomography (TBCT) scans, audiologic tests, and preoperative WOT.
Results: from patients who underwent SS-R.
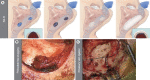
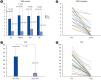
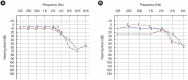
Results: In total, 26 patients were included in the study. The mean age was 44 years, and the mean symptom duration was 3 months. Fourteen patients (53.8%) were completely cured, seven (26.9%) significantly improved, and five (19.2%) remained stable. The mean visual analog scale loudness score decreased from 5.26 to 1.34 (P<0.001) and the mean Tinnitus Handicap Inventory score also improved from 50.23 to 5.5 (P<0.001) after SS-R surgery. In 10 patients with discrepancies between the preoperative TBCT and intraoperative findings, WOT showed a significant additive effect in predicting surgical outcomes. No patients experienced severe intraoperative or postoperative complications during the entire follow-up period.
Conclusion: SS-R provides significant symptom improvement in patients with sigmoid sinus dehiscence who had a positive WOT without other sigmoid sinus variants. A combined diagnostic approach with TBCT, WOT, and intraoperative findings is crucial for achieving better surgical outcomes in patients with PT caused by sigmoid sinus variants.
Keywords: Pulsatile Tinnitus; Surgery; Vascular Origin Tinnitus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transmastoid reshaping of the sigmoid sinus: preliminary study of a novel surgical method to quiet pulsatile tinnitus of an unrecognized vascular origin.J Neurosurg. 2016 Aug;125(2):441-9. doi: 10.3171/2015.6.JNS15961. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26745481
-
Novel technique utilizing polymethylmethacrylate cement for the treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by different sigmoid sinus pathologies.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Feb;282(2):1095-1101. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08974-6. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39306587
-
Prevalence, Surgical Management, and Audiologic Impact of Sigmoid Sinus Dehiscence Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus.Otol Neurotol. 2021 Jan;42(1):82-91. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002846. Otol Neurotol. 2021. PMID: 33301285
-
Surgical management of pulsatile tinnitus secondary to jugular bulb or sigmoid sinus diverticulum with review of literature.Am J Otolaryngol. 2018 Mar-Apr;39(2):247-252. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.12.019. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Am J Otolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29336902 Review.
-
Systematic Review of Temporal Bone-Resurfacing Techniques for Pulsatile Tinnitus Associated with Vascular Wall Anomalies.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 May;160(5):749-761. doi: 10.1177/0194599818823205. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 30667295
Cited by
-
Recent Updates on Tinnitus Management.J Audiol Otol. 2023 Oct;27(4):181-192. doi: 10.7874/jao.2023.00416. Epub 2023 Oct 10. J Audiol Otol. 2023. PMID: 37872753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Personality Traits on the Severity of Chronic Subjective Tinnitus: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 3;60(8):1259. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081259. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202540 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Type 1 Tympanoplasty: Evaluation of Clinical Success and Hearing Improvement.Medeni Med J. 2024 Dec 27;39(4):268-274. doi: 10.4274/MMJ.galenos.2024.88278. Medeni Med J. 2024. PMID: 39726409 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Novel technique utilizing polymethylmethacrylate cement for the treatment of Pulsatile Tinnitus caused by different sigmoid sinus pathologies.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Mar;282(3):1537-1538. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-09123-9. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39668227 No abstract available.
-
Easing the Burden of Tinnitus: A Narrative Review for Exploring Effective Pharmacological Strategies.Cureus. 2024 Feb 25;16(2):e54861. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54861. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38533154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liyanage SH, Singh A, Savundra P, Kalan A. Pulsatile tinnitus. J Laryngol Otol. 2006 Feb;120(2):93–7. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal R, Lloyd S. Pulsatile tinnitus. Otorhinolaryngology. 2012;5(1):7–14.
-
- Kim CS, Kim SY, Choi H, Koo JW, Yoo SY, An GS, et al. Transmastoid reshaping of the sigmoid sinus: preliminary study of a novel surgical method to quiet pulsatile tinnitus of an unrecognized vascular origin. J Neurosurg. 2016 Aug;125(2):441–9. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez TG, Murao M, de Medeiros IR, Kii M, Bento RF, Caldas JG, et al. A new therapeutic procedure for treatment of objective venous pulsatile tinnitus. Int Tinnitus J. 2002;8(1):54–7. - PubMed

