Spatiomolecular Characterization of Dopamine D2 Receptors Cells in the Mouse External Globus Pallidus
- PMID: 37475558
- PMCID: PMC11097984
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666230720121027
Spatiomolecular Characterization of Dopamine D2 Receptors Cells in the Mouse External Globus Pallidus
Abstract
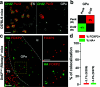
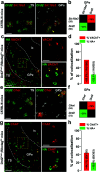
The external globus pallidus (GPe) is part of the basal ganglia circuit and plays a key role in controlling the actions. Although, many evidence indicate that dopamine through its activation of dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) modulates the GPe neuronal activity, the precise spatiomolecular characterization of cell populations expressing D2Rs in the mouse GPe is still lacking. By combining single molecule in situ hybridization, cell type-specific imaging analyses, and electrophysiology slice recordings, we found that GPe D2R cells are neurons preferentially localized in the caudal portion of GPe. These neurons comprising pallido-striatal, pallido-nigral, and pallido-cortical neurons segregate into two distinct populations displaying molecular and electrophysiological features of GPe GABAergic PV/NKX2.1 and cholinergic neurons respectively. By clarifying the spatial molecular identity of GPe D2R neurons in the mouse, this work provides the basis for future studies aiming at disentangling the action of dopamine within the GPe.
Keywords: D2Rs.; Dopamine; cholinergic neurons; globus pallidus; mouse; pallidostriatal.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of external globus pallidus-subthalamic nucleus network dynamics in parkinsonian mice during cortical slow-wave activity and activation.J Physiol. 2020 May;598(10):1897-1927. doi: 10.1113/JP279232. Epub 2020 Apr 23. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32112413 Free PMC article.
-
Npas1+-Nkx2.1+ Neurons Are an Integral Part of the Cortico-pallido-cortical Loop.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 22;40(4):743-768. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1199-19.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 6. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31811030 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of GABAergic neuron subtypes from the globus pallidus using wild-type and transgenic mice.J Physiol. 2018 Sep;596(17):4219-4235. doi: 10.1113/JP276079. Epub 2018 Jul 30. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29917235 Free PMC article.
-
Connectivity and Functionality of the Globus Pallidus Externa Under Normal Conditions and Parkinson's Disease.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Mar 2;15:645287. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.645287. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 33737869 Free PMC article.
-
Cell and circuit complexity of the external globus pallidus.Nat Neurosci. 2023 Jul;26(7):1147-1159. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01368-7. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Nat Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37336974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dodson P.D., Larvin J.T., Duffell J.M., Garas F.N., Doig N.M., Kessaris N., Duguid I.C., Bogacz R., Butt S.J.B., Magill P.J. Distinct developmental origins manifest in the specialized encoding of movement by adult neurons of the external globus pallidus. Neuron. 2015;86(2):501–513. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdi A., Mallet N., Mohamed F.Y., Sharott A., Dodson P.D., Nakamura K.C., Suri S., Avery S.V., Larvin J.T., Garas F.N., Garas S.N., Vinciati F., Morin S., Bezard E., Baufreton J., Magill P.J. Prototypic and arkypallidal neurons in the dopamine-intact external globus pallidus. J. Neurosci. 2015;35(17):6667–6688. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4662-14.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aristieta A., Barresi M., Azizpour L.S., Barrière G., Courtand G., de la Crompe B., Guilhemsang L., Gauthier S., Fioramonti S., Baufreton J., Mallet N.P. A disynaptic circuit in the globus pallidus controls locomotion inhibition. Curr. Biol. 2021;31(4):707–721.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.11.019. - DOI - PubMed

