Broadening the Spectrum of SLC22A5 Phenotype: Primary Carnitine Deficiency Presenting with Focal Myoclonus
- PMID: 37475835
- PMCID: PMC10354736
- DOI: 10.1177/2329048X231184183
Broadening the Spectrum of SLC22A5 Phenotype: Primary Carnitine Deficiency Presenting with Focal Myoclonus
Abstract
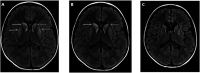
Primary carnitine deficiency (PCD) is caused by pathogenic variants of the SLC22A5 gene, which encodes a transmembrane protein that functions as a high affinity carnitine transporter. Carnitine is essential for the transport of acyl-CoA, produced from fatty acids, into the mitochondria where they are oxidised to produce energy. We present the case history of an 8-year-old boy who presented with fever, lethargy, focal rhythmic (3 Hz) left wrist twitching, and severe encephalopathy. MRI brain showed basal ganglia involvement. Metabolic investigations revealed low serum carnitine; whole genome sequencing confirmed compound heterozygous SLC22A5 mutations. With carnitine replacement, intensive care support, and neurorehabilitation, he made a remarkable recovery, regaining independent breathing, speech, mobility, and hand use. Seizure presentation in PCD is rare and presentation with sustained focal myoclonus has not been previously reported. This case expands the known phenotype of PCD. Prompt carnitine replacement is imperative.
Keywords: focal myoclonus; genotype phenotype; primary carnitine deficiency.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al.Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405‐424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

