An oncolytic adenovirus coding for a variant interleukin 2 cytokine improves response to chemotherapy through enhancement of effector lymphocyte cytotoxicity, fibroblast compartment modulation and mitotic slippage
- PMID: 37475863
- PMCID: PMC10354511
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171083
An oncolytic adenovirus coding for a variant interleukin 2 cytokine improves response to chemotherapy through enhancement of effector lymphocyte cytotoxicity, fibroblast compartment modulation and mitotic slippage
Abstract
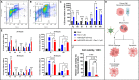
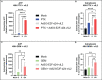
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly treatment-resistant cancer. Currently, the only curative treatment for PDAC is surgery, but most patients are diagnosed with metastatic disease and thus outside the scope of surgery. The majority of metastatic patients receive chemotherapy, but responses are limited. New therapeutics are thus urgently needed for PDAC. One major limitation in treating PDAC has been the highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) which inhibits anti-cancer immune responses. We have constructed an oncolytic adenovirus coding for a variant the interleukin 2 molecule, Ad5/3-E2F-d24-vIL2 (also known as TILT-452, and "vIL-2 virus"), with preferential binding to IL-2 receptors on the surface of effector lymphocytes over T regulatory cells (T regs). In the present study this virus was evaluated in combination with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine chemotherapy in Panc02 mouse model. Ad5/3-E2F-d24-vIL2 showed marked PDAC cell killing in vitro, alongside induction of mitotic slippage and immunogenic cell death in PDAC cell lines, when combined with chemotherapy. Increased survival was seen in vivo with 80% of animals surviving long term, when compared to chemotherapy alone. Moreover, combination therapy mediated enhanced tumor growth control, without observable toxicities in internal organs or external features. Survival and tumor control benefits were associated with activation of tumor infiltrating immune cells, downregulation of inhibitory signals, change in fibroblast populations in the tumors and changes in intratumoral cytokines, with increased chemokine amounts (CCL2, CCL3, CCL4) and anti-tumor cytokines (IFN-γ and TNFα). Furthermore, vIL-2 virus in combination with chemotherapy efficiently induced tumor protection upon rechallenge, that was extended to a previously non-encountered cancer cell line. In conclusion, Ad5/3-E2F-d24-vIL2 is a promising immunotherapy candidate when combined with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine.
Keywords: adenovirus; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; interleukin 2; oncolytic virus.
Copyright © 2023 Pakola, Quixabeira, Kudling, Clubb, Grönberg-Vähä-Koskela, Basnet, Jirovec, Arias, Haybout, Heiniö, Santos, Cervera-Carrascon, Havunen, Anttila and Hemminki.
Conflict of interest statement
AH is a shareholder in Targovax ASA. AH, JC, VCC, JMS are an employees and shareholders in TILT Biotherapeutics Ltd. DQ, EJ, LH, RH are employees of TILT Biotherapeutics Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

