Time-integrated Cumulative Parameters Predictive of Radiographic Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Real-world Data From a Prospective Single-center Cohort
- PMID: 37475902
- PMCID: PMC10327621
- DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.98
Time-integrated Cumulative Parameters Predictive of Radiographic Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Real-world Data From a Prospective Single-center Cohort
Abstract
Objective: With many chronic inflammatory diseases, outcomes are determined by assessing both disease activity at presentation and cumulative activity over time. Here, we investigated whether cumulative activity better reflects the radiographic progression (RP) of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) than measurement of activity at a single time point.
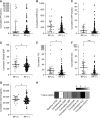
Methods: From a prospective cohort of RA patients, most of whom were treated with anti-rheumatic drugs, we selected 117 subjects for whom laboratory, clinical, and radiographic parameters potentially influencing RP were monitored serially for more than 1 year. X-ray images of both hands and both feet were scored using the van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (mTSS). In addition to cross-sectional values at baseline, longitudinal and cumulative values for each parameter were calculated in a time-integrated and averaged manner.
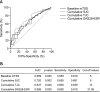
Results: Among the values measured at baseline, mTSS, but not the baseline erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein level, was associated with RP. By contrast, multivariate analyses identified cumulative values such as the cumulative ESR, cumulative tender joint count, cumulative swollen joint count (SJC), and cumulative Disease Activity Score 28-ESR as major determinants of RP. In particular, the cumulative SJC showed the best predictive performance for RP.
Conclusion: This study highlights the importance of cumulative indices for predicting progression of RA. Specifically, dynamic and cumulative values of RA activity-related factors, particularly the cumulative SJC, may be the major determinants of RP in the current practice.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Prognosis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 by The Korean College of Rheumatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Oh YJ, Park B, Moon KW. Effect of drug adherence on treatment outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 2019;26:264–72. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.264. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
