Clinical and Genetic Risk Factors Associated With the Presence of Lupus Nephritis
- PMID: 37475996
- PMCID: PMC10324894
- DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.3.150
Clinical and Genetic Risk Factors Associated With the Presence of Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate whether clinical features and the weighted genetic risk score (wGRS) were associated with the presence of lupus nephritis (LN).
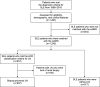
Methods: We retrospectively divided patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, n=1,078) into biopsy-proven LN (n=507) and non-LN groups (non-LN, n=571) Baseline clinical features, serologic markers, and the wGRS were collected The wGRS was calculated from 112 non-human leukocyte antigen (non-HLA) loci and HLA-DRβ1 amino acid haplotypes for SLE Associations among clinical features, wGRS, and the presence of LN were identified.
Results: In the multivariate analysis, patients with LN were younger at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR]=0.97, p<0.001), had more pleuritis (OR=2.44, p<0.001) and pericarditis (OR=1.62, p=0.029), had a higher detection rate of anti-double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (anti-dsDNA antibodies, OR=2.22, p<0.001), anti-Smith antibodies (anti-Sm antibodies, OR=1.70, p=0.002), low level of complement (OR=1.37, p=0.043) and absence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL antibodies, OR=1.60, p=0.002), and had higher wGRS (OR=1.16, p=0.012) Mediation analysis suggested that anti-Sm antibodies and low complement could be mediators in the relationship between high wGRS and the presence of LN.
Conclusion: Onset age, pleuritis, pericarditis, several serologic markers, and wGRS were associated with the presence of LN Anti-Sm antibodies and low complement appeared to mediate the indirect relationship between wGRS and the presence of LN.
Keywords: Associated factors; Genetic risk score; Lupus nephritis; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean College of Rheumatology. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-Smith Antibodies as a Predictive Factor for Developing Lupus Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 6;16(8):e66270. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66270. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39238683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higher Genetic Risk Loads Confer More Diverse Manifestations and Higher Risk of Lupus Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Sep;75(9):1566-1572. doi: 10.1002/art.42516. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37011055
-
Immunological aspects of biopsy-proven lupus nephritis in Bahraini patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2013 Nov;24(6):1271-9. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.121286. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2013. PMID: 24231503
-
Interactions Between Genome-Wide Genetic Factors and Smoking Influencing Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Nov;72(11):1863-1871. doi: 10.1002/art.41414. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32969204 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus nephritis in Colombians: contrasts and comparisons with other populations.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;40(3):199-207. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8249-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21287296 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus genetics: insights into pathogenesis and implications for therapy.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;20(10):635-648. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01152-2. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39232240 Review.
-
Association between Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematous and Polymorphisms in miR-146a and miR-499: A Meta-Analysis.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2023;184(8):814-821. doi: 10.1159/000527575. Epub 2023 May 11. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37231940 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Biological Agents in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis: A Network Meta-Analysis.Pharmacology. 2023;108(1):17-26. doi: 10.1159/000527223. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Pharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36327917 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating the Risk of Lupus Nephritis: How Far Have We Come?J Rheum Dis. 2021 Oct 1;28(4):173-175. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.173. J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 37476364 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Anti-Smith Antibodies as a Predictive Factor for Developing Lupus Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 6;16(8):e66270. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66270. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39238683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
