Is playing violent video games a risk factor for aggressive behaviour? Adding narcissism, self-esteem and PEGI ratings to the debate
- PMID: 37476087
- PMCID: PMC10354552
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1155807
Is playing violent video games a risk factor for aggressive behaviour? Adding narcissism, self-esteem and PEGI ratings to the debate
Abstract
Introduction: Aggressive behaviour is a challenge for society. There continues to be considerable debate over whether the consumption of violent video games affects aggression, as violent video game content has become more accessible in recent years due to the growing use of online distribution platforms. Personality traits often linked to aggression, such as narcissism and self-esteem, have been considered in the context of violent video game play and their relationship with aggression.
Methods: We surveyed an international population of 166 game players on their personality traits and their three favourite video game choices, which were classified as violent or non-violent, using Pan European Game Information (PEGI) 16 and 18 ratings.
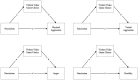
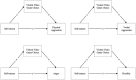
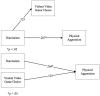
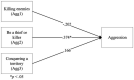
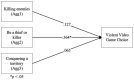
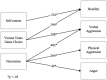
Results: We found that violent video game choice is a predictor of verbal aggression alongside narcissism, and hostility alongside self-esteem. A categorical regression highlighted the desire to impersonate society's undesirable role models (e.g., 'be a thief or a killer') as one of the motivations for aggression and violent video game choice.
Discussion: These findings show that video game violence should be considered a risk factor for aggression, as in other violent media, as it provides a social reinforcement of aggressive behaviour and observational learning of aggressive models, calling for the introduction of stricter online age verification procedures on online game platforms to safeguard children from violent video game content; and increased use of parental controls on content fruition. More granularity should be considered in the PEGI classifications.
Keywords: aggressive behaviour; narcissism; self-esteem; social psychology; violent video games.
Copyright © 2023 Olejarnik and Romano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Why do habitual violent video game players believe in the cathartic effects of violent video games? A misinterpretation of mood improvement as a reduction in aggressive feelings.Aggress Behav. 2022 Mar;48(2):219-231. doi: 10.1002/ab.22005. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Aggress Behav. 2022. PMID: 34743352 Free PMC article.
-
The lone gamer: Social exclusion predicts violent video game preferences and fuels aggressive inclinations in adolescent players.Aggress Behav. 2018 Mar;44(2):113-124. doi: 10.1002/ab.21735. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Aggress Behav. 2018. PMID: 29052252
-
Effects of playing a violent video game as male versus female avatar on subsequent aggression in male and female players.Aggress Behav. 2014 Nov-Dec;40(6):537-41. doi: 10.1002/ab.21551. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Aggress Behav. 2014. PMID: 25043905 Clinical Trial.
-
Video games do affect social outcomes: a meta-analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play.Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2014 May;40(5):578-89. doi: 10.1177/0146167213520459. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2014. PMID: 24458215 Review.
-
The dark and bright side of video game consumption: Effects of violent and prosocial video games.Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Aug;46:101326. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2022.101326. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35366605 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of video game consumption habits in the relationship between gender and attitudes towards violence among adolescents.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95555-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681636 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Game Addiction and Aggression among Adolescents with Mediating Role of Narcissism and Self-Control.Iran J Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;19(3):274-284. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v19i3.15804. Iran J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39055523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agustarika B., Adam A. (2020). The effect of online gaming addiction on violent behavior of high school students in Sorong City. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 11, 1534–1538.
-
- Ames D. R., Rose P., Anderson C. P. (2006). The NPI-16 as a short measure of narcissism. J. Res. Pers. 40, 440–450. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2005.03.002 - DOI
-
- Anderson M.. (2016) Parents, teens and digital monitoring, pew research center. Available at: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2016/01/07/parents-teens-and-digita... (accessed February 17, 2022)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

