Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction Among Adolescent Athletes With Asthma: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37476118
- PMCID: PMC10355688
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.40643
Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction Among Adolescent Athletes With Asthma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
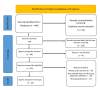
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB) is a concern that frequently affects athletes and regular exercisers. The main objective of this systematic review is to study recently published literature that evaluated the risk of EIB among adolescent athletes with asthma. PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, EBSCO, SCOPUS, Wiley, and Cochrane Library were searched. Study articles were screened by title and abstract using Rayyan QCRI then a full-text assessment was implemented. A total of ten studies with 3129 adolescent athletic subjects were included in this review. The prevalence of EIB ranged from 2.1% to 61%. Most studies have demonstrated that athletes in their adolescence suffer from EIB, which requires regular management. Two studies have reported that low-income communities and humidity levels are risk factors for EIB. We found that EIB is frequent among adolescent athletes. The prevalence varies between countries due to different social and environmental factors.
Keywords: a systematic review; adolescents; asthma; athletes; exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
Copyright © 2023, Hashim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. [ Jan; 2023 ];https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma 2020 18:2023.
-
- Letter to the editor: the evidence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in endurance runners; genetic basis and gender differences. Abbasi A, Vieira RdP, Northoff H. https://europepmc.org/article/med/25828753. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2015;21:186–188. - PubMed
-
- Winter sports athletes: long-term effects of cold air exposure. Sue-Chu M. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46:397–401. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources