The Duration of Postoperative Antibiotics in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37476125
- PMCID: PMC10355167
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.40631
The Duration of Postoperative Antibiotics in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
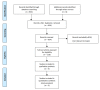
Although prophylactic antibiotic use following autologous breast reconstruction post-mastectomy is a common practice, there is no consensus in the literature regarding its duration. Antibiotic stewardship is important to minimise multi-resistant organisms as well as mitigate the associated side effects. Currently, there are no published guidelines regarding the duration of prophylactic antibiotics in autologous breast reconstruction surgery following mastectomy. The authors searched the online literature regarding the administration of antibiotics for autologous breast reconstruction surgery post-mastectomy. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines were followed. The primary outcome measure was the incidence of surgical site infections (SSIs). Three studies met the inclusion criteria and included a total of 1,400 patients. Overall, 101 (7.2%) SSIs were observed. There was no significant difference in the rate of SSIs when comparing the use of antibiotics for less than or longer than 24 hours postoperatively (odds ratio = 1.434, p = 0.124). There is no significant difference between SSIs with the use of antibiotics for longer than 24 hours when compared to less than 24 hours. Further studies in the form of randomised controlled trials are required to assess the effects of prophylactic antibiotic duration in autologous breast reconstruction following mastectomy.
Keywords: autologous breast reconstruction; oncoplastic breast surgery; perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis; reconstructive breast surgery; surgical site infection (ssi).
Copyright © 2023, Aldarragi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
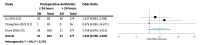
References
-
- Dynamic changes in quality of life, psychological status, and body image in women who underwent a mastectomy as compared with breast reconstruction: an 8-year follow up. Konara Mudiyanselage SP, Wu YL, Kukreti S, et al. Breast Cancer. 2023;30:226–240. - PubMed
-
- Radiotherapy and breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Barry M, Kell MR. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;127:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Hospital-associated costs due to surgical site infection after breast surgery. Olsen MA, Chu-Ongsakul S, Brandt KE, Dietz JR, Mayfield J, Fraser VJ. Arch Surg. 2008;143:53–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
