High Expression of Microtubule-associated Protein TBCB Predicts Adverse Outcome and Immunosuppression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 37476188
- PMCID: PMC10355208
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.84215
High Expression of Microtubule-associated Protein TBCB Predicts Adverse Outcome and Immunosuppression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
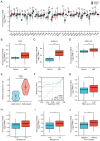
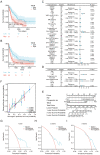
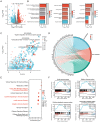
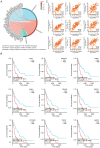
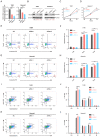
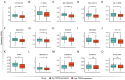
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a devastating blood cancer with high heterogeneity and ill-fated outcome. Despite numerous advances in AML treatment, the prognosis remains poor for a significant proportion of patients. Consequently, it is necessary to accurately and comprehensively identify biomarkers as soon as possible to enhance the efficacy of diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of AML. In this study, we aimed to identify prognostic markers of AML by analyzing the cohorts from TCGA-LAML database and GEO microarray datasets. Interestingly, the transcriptional level of microtubule-associated protein TBCB in AML patients was noticeably increased when compared with normal individuals, and this was verified in two independent cohorts (GSE9476 and GSE13159) and with our AML patients. Furthermore, univariate and multivariate regression analysis revealed that high TBCB expression was an independent poor prognostic factor for AML. GO and GSEA enrichment analysis hinted that immune-related signaling pathways were enriched in up-regulated DEGs between two populations separated by the median expression level of TBCB. By constructing a protein-protein interaction network, we obtained six hub genes, all of which are immune-related molecules, and their expression levels were positively linked to that of TBCB. In addition, the high expression of three hub genes was significantly associated with a poor prognosis in AML. Moreover, we found that the tumor microenvironment in AML with high TBCB expression tended to be infiltrated by NK cells, especially CD56bright NK cells. The transcriptional levels of NK cell inhibitory receptors and their ligands were positively related to that of TBCB, and their high expression levels also predicted poor prognosis in AML. Notably, we found that the down-regulation of TBCB suppressed cell proliferation in AML cell lines by enhancing the apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Finally, drug sensitivity prediction illustrated that cells with high TBCB expression were more responsive to ATRA and midostaurin but resistant to cytarabine, dasatinib, and imatinib. In conclusion, our findings shed light on the feasibility of TBCB as a potential predictor of poor outcome and to be an alternative target of treatment in AML.
Keywords: TBCB; acute myeloid leukemia; bioinformatics; drug sensitivity; immune evasion; prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low expression of the metabolism-related gene SLC25A21 predicts unfavourable prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 30;13:970316. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.970316. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246603 Free PMC article.
-
High-expression of the innate-immune related gene UNC93B1 predicts inferior outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 18;14:1063227. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1063227. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36741319 Free PMC article.
-
[Prognostic implications and functional enrichment analysis of LTB4R in patients with acute myeloid leukemia].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Mar 20;42(3):309-320. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.03.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35426793 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Integrated bioinformatic analysis of mitochondrial metabolism-related genes in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1120670. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1120670. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37138869 Free PMC article.
-
GPX1-associated prognostic signature predicts poor survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and involves in immunosuppression.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Jan 1;1868(1):166268. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166268. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 34536536
Cited by
-
Isoform-Level Transcriptome Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Breast Cancer Patients Identifies a Disease-Associated RASGEF1A Isoform.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 16;16(18):3171. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183171. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335143 Free PMC article.
-
RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Mar 28;20(1):20251168. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1168. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40177653 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

