KOBIO, the First Web-based Korean Biologics Registry Operated With a Unified Platform Among Distinct Disease Entities
- PMID: 37476366
- PMCID: PMC10324910
- DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.176
KOBIO, the First Web-based Korean Biologics Registry Operated With a Unified Platform Among Distinct Disease Entities
Abstract
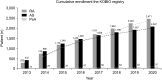
The KOrean College of Rheumatology BIOlogics and targeted therapy (KOBIO) registry is a nationwide observational cohort that captures detailed data on exposure of patients to biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). This registry was launched in December 2012 with an aim to prospectively investigate clinical manifestations and outcomes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis who initiated a biologic or targeted synthetic DMARD or switched to another. Demographic data, disease activity, current treatment, adverse events, terms based on Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities, and so on are registered for patients who are then followed up annually in a web-based unified platform. The KOBIO registry also recruits and collects data of patients with RA on conventional DMARDs for comparison. As of today, more than 5,500 patients were enrolled from 47 academic and community Rheumatology centers across Korea. The KOBIO registry has evolved to become a powerful database for clinical research to improve clinical outcomes and quality of treatment.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Biological products; Psoriatic arthritis; Registries; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean College of Rheumatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Gliklich RE, Dreyer NA, Leavy MB. Patient registries. In: Gliklich RE, Dreyer NA, Leavy MB, editors. Registries for evaluating patient outcomes: a user's guide. 3rd ed. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); Rockville (MD): 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
