Feasibility of diffusion kurtosis imaging in evaluating cervical spinal cord injury in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 37478237
- PMCID: PMC10662919
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034205
Feasibility of diffusion kurtosis imaging in evaluating cervical spinal cord injury in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
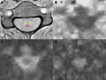
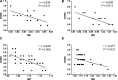
This research aimed to assess gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), lesions of multiple sclerosis (MS) and the therapeutic effect using diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI). From January 2018 to October 2019, 78 subjects (48 of MS and 30 of health) perform routine MR scan and DKI of cervical spinal cord. The MS patients were divided into 2 groups according to the presence or absence of T2 hyperintensity. DKI-metrics were measured in the lesions, normal-appearing GM and WM. Significant differences were detected in DKI metrics between MS and healthy (P < .05) and between patients with cervical spinal cord T2-hyperintense and without T2-hyperintense (P < .001). Compared to healthy, GM-mean kurtosis (MK), GM-radial kurtosis, and WM-fractional anisotropy, WM-axial diffusion were statistically reduced in patients without T2-hyperintense (P < .05). Significant differences were observed in DKI metrics between patients with T2-hyperintense after therapy (P < .05), as well as GM-MK and WM-fractional anisotropy, WM-axial diffusion in patients without T2-hyperintense (P < .05); Expanded Disability Status Scale was correlated with MK values, as well as Expanded Disability Status Scale scores and MK values after therapy. Our results indicate that DKI-metrics can detect and quantitatively evaluate the changes in cervical spinal cord micropathological structure.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of microstructural changes in spinal cord of patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy by diffusion kurtosis imaging and investigate the correlation with JOA score.BMC Neurol. 2020 May 13;20(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01752-x. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32404188 Free PMC article.
-
A better characterization of spinal cord damage in multiple sclerosis: a diffusional kurtosis imaging study.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Sep;34(9):1846-52. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3512. Epub 2013 Apr 11. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 23578677 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations between cervical spinal cord magnetic resonance diffusion tensor and diffusion kurtosis imaging metrics and motor performance in patients with chronic ischemic brain lesions of the corticospinal tract.Neuroradiology. 2019 Feb;61(2):175-182. doi: 10.1007/s00234-018-2139-5. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Neuroradiology. 2019. PMID: 30519889
-
Application value of diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) in evaluating microstructural changes in the spinal cord of patients with early cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017 May;156:71-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28349894
-
Advanced Diffusion MR Imaging for Multiple Sclerosis in the Brain and Spinal Cord.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2022 Mar 1;21(1):58-70. doi: 10.2463/mrms.rev.2021-0091. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35173096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of the left uncinate fasciculus in the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an exploratory longitudinal multi-modal neuroimaging and neuropsychological study.Brain Struct Funct. 2024 Dec 17;230(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00429-024-02884-3. Brain Struct Funct. 2024. PMID: 39688717
References
-
- Stenager E. A global perspective on the burden of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:227–8. - PubMed
-
- Ciccarelli O, Cohen JA, Reingold SC, et al. .; International Conference on Spinal Cord Involvement and Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Spinal cord involvement in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:185–97. - PubMed
-
- Filippi M, Rocca MA. Novel MRI approaches to assess patients with multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2010;23:212–7. - PubMed
-
- Kearney H, Yiannakas MC, Samson RS, et al. . Investigation of magnetization transfer ratio-derived pial and subpial abnormalities in the multiple sclerosis spinal cord. Brain. 2014;137:2456–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

