Loss of SYNCRIP unleashes APOBEC-driven mutagenesis, tumor heterogeneity, and AR-targeted therapy resistance in prostate cancer
- PMID: 37478850
- PMCID: PMC10530398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.06.010
Loss of SYNCRIP unleashes APOBEC-driven mutagenesis, tumor heterogeneity, and AR-targeted therapy resistance in prostate cancer
Abstract
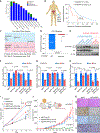
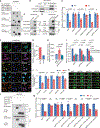
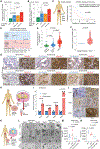
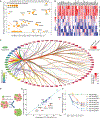
Tumor mutational burden and heterogeneity has been suggested to fuel resistance to many targeted therapies. The cytosine deaminase APOBEC proteins have been implicated in the mutational signatures of more than 70% of human cancers. However, the mechanism underlying how cancer cells hijack the APOBEC mediated mutagenesis machinery to promote tumor heterogeneity, and thereby foster therapy resistance remains unclear. We identify SYNCRIP as an endogenous molecular brake which suppresses APOBEC-driven mutagenesis in prostate cancer (PCa). Overactivated APOBEC3B, in SYNCRIP-deficient PCa cells, is a key mutator, representing the molecular source of driver mutations in some frequently mutated genes in PCa, including FOXA1, EP300. Functional screening identifies eight crucial drivers for androgen receptor (AR)-targeted therapy resistance in PCa that are mutated by APOBEC3B: BRD7, CBX8, EP300, FOXA1, HDAC5, HSF4, STAT3, and AR. These results uncover a cell-intrinsic mechanism that unleashes APOBEC-driven mutagenesis, which plays a significant role in conferring AR-targeted therapy resistance in PCa.
Keywords: APOBEC; AR-targeted therapy resistance; EP300; FOXA1; SYNCRIP; antiandorgen; mutagenesis; prostate cancer; tumor heterogeneity.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.M. served as a scientific consultant to Accutar Biotechnology, Inc. G.V.R. holds issued and pending patents, which have been licensed to EtiraRx. G.V.R. serves or has served in an advisory role to Bayer, Johnson and Johnson, Myovant, EtiraRx, Amgen, Pfizer, and Astellas. He has or has had grant support from Bayer, EtiraRx, and Johnson and Johnson. T.W. is a scientific co-founder of NightStar Biotechnologies, Inc. H.L. is a shareholder and scientific advisor of Precision Scientific Ltd.
Figures


Comment in
-
New insights into APOBEC-mediated mutagenesis in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2023 Sep;20(9):519. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00808-0. Nat Rev Urol. 2023. PMID: 37553529 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dagogo-Jack I, and Shaw AT (2018). Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 81–94. - PubMed
-
- Stewart CA, Gay CM, Xi Y, Sivajothi S, Sivakamasundari V, Fujimoto J, Bolisetty M, Hartsfield PM, Balasubramaniyan V, Chalishazar MD, et al. (2020). Single-cell analyses reveal increased intratumoral heterogeneity after the onset of therapy resistance in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 1, 423–436. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

