Effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on endothelial function in individuals with overweight and obesity: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 37479727
- PMCID: PMC10362025
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38603-x
Effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on endothelial function in individuals with overweight and obesity: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Abstract
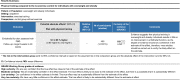
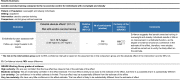
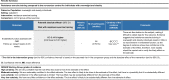
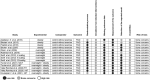
The objective of this systematic review was to examine the effects of exercise training on endothelial function in individuals with overweight and obesity. Our review study included only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving adults (≥ 18 years of age) with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25.0 kg/m2. Our search was conducted in the electronic bases MEDLINE (PubMed), Cochrane, LILACS and EMBASE and in the gray literature. We performed random-effects analyses for effect estimates and used 95% prediction intervals (95% PI) for estimating the uncertainty of the study results. There were selected 10 RCTs involving 14 groups (n = 400). The quality assessment of studies using Cochrane risk-of-bias 2 (RoB 2) tool identified some concerns. Exercise training resulted in improved flow-mediated dilation (FMD) in individuals with overweight and obesity (p < 0.001) compared to the no-exercise control group. This effect of training modalities on FMD was seen for aerobic training (p < 0.001) but not for resistance training (p = 0.051). There was no difference in FMD in response to exercise training by BMI classification (overweight, obesity, overweight + obesity), p = 0.793. The present results are consistent with the notion that aerobic exercise training elicits favorable adaptations in endothelial function in individuals with overweight and obesity. Our findings should be interpreted with caution because of the small number of studies included in this review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of regular aerobic exercise on vascular function in overweight or obese older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Exerc Sci Fit. 2023 Oct;21(4):313-325. doi: 10.1016/j.jesf.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2023. PMID: 37520931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Physical Training Programs on Physical Fitness in People With Class II and III Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Phys Ther. 2020 Jun 23;100(6):963-978. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzaa045. Phys Ther. 2020. PMID: 32211862
-
Effects of aerobic, resistance and combined training on endothelial function and arterial stiffness in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0308600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308600. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621701 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic exercise and resistance exercise on physical indexes and cardiovascular risk factors in obese and overweight school-age children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 20;16(9):e0257150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257150. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34543302 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Exercise Training Under Normobaric Hypoxic Conditions to Improve Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.High Alt Med Biol. 2023 Dec;24(4):312-320. doi: 10.1089/ham.2022.0099. High Alt Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 38127802
Cited by
-
Time-of-Day-Dependent Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Carotid Hemodynamics in Sedentary Adults.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jun 17;14(6):713. doi: 10.3390/biology14060713. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563963 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular, Hemodynamic, and Anthropometric Adaptations Induced by Walking Training at FATmax in Obese Males and Females over 45 Years Old.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Apr 29;22(5):701. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050701. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40427817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen MD, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;63:2985–3023. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

