Distinct Requirements for Adaptor Proteins NCK1 and NCK2 in Mammary Gland Development
- PMID: 37479911
- PMCID: PMC10361900
- DOI: 10.1007/s10911-023-09541-1
Distinct Requirements for Adaptor Proteins NCK1 and NCK2 in Mammary Gland Development
Abstract
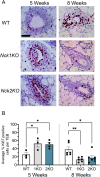
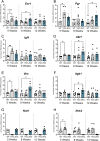
The adaptor proteins NCK1 and NCK2 are well-established signalling nodes that regulate diverse biological processes including cell proliferation and actin dynamics in many tissue types. Here we have investigated the distribution and function of Nck1 and Nck2 in the developing mouse mammary gland. Using publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing data, we uncovered distinct expression profiles between the two paralogs. Nck1 showed widespread expression in luminal, basal, stromal and endothelial cells, while Nck2 was restricted to luminal and basal cells, with prominent enrichment in hormone-sensing luminal subtypes. Next, using mice with global knockout of Nck1 or Nck2, we assessed mammary gland development during and after puberty (5, 8 and 12 weeks of age). Mice lacking Nck1 or Nck2 displayed significant defects in ductal outgrowth and branching at 5 weeks compared to controls, and the defects persisted in Nck2 knockout mice at 8 weeks before normalizing at 12 weeks. These defects were accompanied by an increase in epithelial cell proliferation at 5 weeks and a decrease at 8 weeks in both Nck1 and Nck2 knockout mice. We also profiled expression of several key genes associated with mammary gland development at these timepoints and detected temporal changes in transcript levels of hormone receptors as well as effectors of cell proliferation and migration in Nck1 and Nck2 knockout mice, in line with the distinct phenotypes observed at 5 and 8 weeks. Together these studies reveal a requirement for NCK proteins in mammary gland morphogenesis, and suggest that deregulation of Nck expression could drive breast cancer progression and metastasis.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; Branching morphogenesis; Knockout mice; Mammary gland development; NCK.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nck1 regulates the in vitro development of human regulatory T cells through AKT pathway.Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jan 21;219(1):uxaf011. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxaf011. Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39963999
-
Endothelial NCK2 promotes atherosclerosis progression in male but not female Nck1-null atheroprone mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 12;9:955027. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.955027. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035930 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of the RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor Net1 to polyoma middle T antigen-mediated mammary gland tumorigenesis and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 May 16;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0966-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29769144 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
The Gene Expression Profile of Milk Somatic Cells of Small Ruminant Lentivirus-Seropositive and -Seronegative Dairy Goats (Capra hircus) During Their First Lactation.Viruses. 2025 Jul 3;17(7):944. doi: 10.3390/v17070944. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

