Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for refractory OHCA: lessons from three randomized controlled trials-the trialists' view
- PMID: 37480551
- PMCID: PMC10449372
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuad071
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for refractory OHCA: lessons from three randomized controlled trials-the trialists' view
Abstract
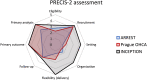
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a promising treatment for refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Three recent randomized trials (ARREST trial, Prague OHCA study, and INCEPTION trial) that addressed the clinical benefit of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest yielded seemingly diverging results. The evidence for extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, derived from three recent randomized controlled trials, is not contradictory but rather complementary. Excellent results can be achieved with a very high level of dedication, provided that strict selection criteria are applied. However, pragmatic implementation of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation does not necessarily lead to improved outcome of refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Centres that are performing extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest or aspire to do so should critically evaluate whether they are able to meet the pre-requisites that are needed to conduct an effective extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation programme.
Keywords: Efficacy and effectiveness; Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Randomized controlled trials; Review.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: R.L. reports a relationship with Medtronic, Getinge, and LivaNova that includes: consulting; and is an Advisory Board Member of Eurosets (honoraria paid as research funding). J.B. reports a relationship with Getinge, Abiomed, Xenios and Medtronic that includes consulting. The remaining authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Downing J, Al Falasi R, Cardona S, Fairchild M, Lowie B, Chan C, et al. . How effective is extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med 2022;51:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Belohlavek J, Kucera K, Jarkovsky J, Franek O, Pokorna M, Danda J, et al. . Hyperinvasive approach to out-of hospital cardiac arrest using mechanical chest compression device, prehospital intraarrest cooling, extracorporeal life support and early invasive assessment compared to standard of care. A randomized parallel groups comparative study proposal. “Prague OHCA study”. J Transl Med 2012;10:163. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

