Ventral Hippocampal Input to Infralimbic Cortex Is Necessary for the Therapeutic-Like Effects of Extinction in Stressed Rats
- PMID: 37480574
- PMCID: PMC10464924
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyad043
Ventral Hippocampal Input to Infralimbic Cortex Is Necessary for the Therapeutic-Like Effects of Extinction in Stressed Rats
Abstract
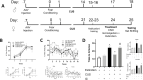
Background: Posttraumatic stress disorder is characterized by deficits in cognitive flexibility related to dysfunction of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Exposure therapy can effectively reverse these deficits. Fear extinction in rodents bears similarity to exposure therapy. Extinction reverses chronic stress-induced deficits in cognitive flexibility on the attentional set-shifting test (AST), an mPFC-mediated process. This therapeutic effect requires activity of pyramidal neurons and brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling in infralimbic cortex (IL). However, the circuit mechanisms governing BDNF-mediated plasticity initiated by extinction in IL are unknown. The ventral hippocampus (vHipp) plays a role in regulating IL activity during extinction, and plasticity in vHipp is necessary for extinction memory consolidation. Therefore, we investigated the role of vHipp input to IL in the effects of extinction in reversing stress-induced cognitive deficits.
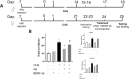
Methods: vHipp input to IL was silenced using a Gi-Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADD) via local infusion of clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) into IL before extinction. A day later, rats were tested on AST. In a separate experiment, we tested whether vHipp input to the IL induces BDNF signaling to exert therapeutic effects. We activated the vHipp using a Gq-DREADD, and injected an anti-BDNF neutralizing antibody into IL. Rats were tested on the AST 24 hours later.
Results: Silencing the vHipp input to IL prevented the beneficial effects of extinction in reversing stress-induced cognitive deficits. Activating vHipp input to IL in the absence of extinction was sufficient to reverse stress-induced deficits in set-shifting. The beneficial effects were blocked by local infusion of a neutralizing anti-BDNF antibody into IL.
Conclusions: vHipp-driven BDNF signaling in IL is critical for extinction to counteract the deleterious cognitive effects of chronic stress.
Keywords: Chronic stress; fear extinction; infralimbic cortex; ventral hippocampus.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activity in the Ventral Medial Prefrontal Cortex Is Necessary for the Therapeutic Effects of Extinction in Rats.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 7;38(6):1408-1417. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0635-17.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29335360 Free PMC article.
-
Infralimbic BDNF signaling is necessary for the beneficial effects of extinction on set shifting in stressed rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Jan;47(2):507-515. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01171-7. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 34497360 Free PMC article.
-
Parvalbumin-Positive Interneurons in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Regulate Stress-Induced Fear Extinction Impairments in Male and Female Rats.J Neurosci. 2023 May 31;43(22):4162-4173. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1442-22.2023. Epub 2023 May 1. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37127359 Free PMC article.
-
A Rodent Model of Exposure Therapy: The Use of Fear Extinction as a Therapeutic Intervention for PTSD.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Mar 11;13:46. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00046. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30914932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical studies of stress, extinction, and prefrontal cortex: intriguing leads and pressing questions.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):59-72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5023-4. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30225660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of chronic stress on cognitive function - From neurobiology to intervention.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Sep 2;33:100670. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100670. eCollection 2024 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 39295772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of extinction require hippocampal input and BDNF signaling in IL.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Nov;50(1):355-356. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01948-6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39085427 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

