Revisiting the origin of the bending in group 2 metallocenes AeCp2 (Ae = Be-Ba)
- PMID: 37482883
- PMCID: PMC10395002
- DOI: 10.1039/d2cp05020j
Revisiting the origin of the bending in group 2 metallocenes AeCp2 (Ae = Be-Ba)
Abstract
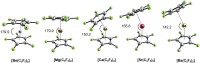
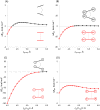
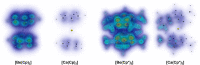
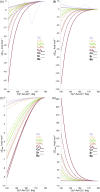
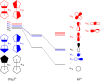
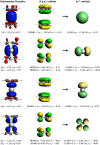
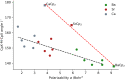
Metallocenes are well-established compounds in organometallic chemistry, and can exhibit either a coplanar structure or a bent structure according to the nature of the metal center (E) and the cyclopentadienyl ligands (Cp). Herein, we re-examine the chemical bonding to underline the origins of the geometry and stability observed experimentally. To this end, we have analysed a series of group 2 metallocenes [Ae(C5R5)2] (Ae = Be-Ba and R = H, Me, F, Cl, Br, and I) with a combination of computational methods, namely energy decomposition analysis (EDA), polarizability model (PM), and dispersion interaction densities (DIDs). Although the metal-ligand bonding nature is mainly an electrostatic interaction (65-78%), the covalent character is not negligible (33-22%). Notably, the heavier the metal center, the stronger the d-orbital interaction with a 50% contribution to the total covalent interaction. The dispersion interaction between the Cp ligands counts only for 1% of the interaction. Despite that orbital contributions become stronger for heavier metals, they never represent the energy main term. Instead, given the electrostatic nature of the metallocene bonds, we propose a model based on polarizability, which faithfully predicts the bending angle. Although dispersion interactions have a fair contribution to strengthen the bending angle, the polarizability plays a major role.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
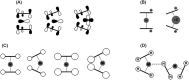
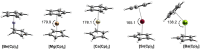

References
-
- Kealy T. J. Pauson P. L. Nature. 1951;168:1039–1040. doi: 10.1038/1681039b0. - DOI
-
- Miller S. A. Tebboth J. A. Tremaine J. F. J. Chem. Soc. 1952:632–635. doi: 10.1039/JR9520000632. - DOI
-
- Fischer E. O. Pfab W. Z. Naturforsch. B. 1952;7:377–379. doi: 10.1515/znb-1952-0701. - DOI
-
- Eiland P. F. Pepinsky R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952;74:4971. doi: 10.1021/ja01139a527. - DOI
-
- Dunitz J. D. Orgel L. E. Nature. 1953;171:121–122. doi: 10.1038/171121a0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

