Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccinations: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37485047
- PMCID: PMC10361396
- DOI: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1605526
Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccinations: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This umbrella meta-analysis aims to provide comprehensive and synthesized evidence regarding the effectiveness and safety of COVID-19 vaccinations based on current studies. Methods: Studies from the Cochrane Library, PubMed, and EMBASE, published before 10 December 2021, were included in the analysis. The pooled results of effectiveness and safety were estimated and shown in forest plots. Results: We included nineteen studies (fifteen studies regarding safety and nine regarding effectiveness) in the analysis. The mRNA vaccines, adenovirus vector vaccines, subunit vaccines, and inactivated vaccines were found to be effective; however, mRNA vaccines, adenovirus vector vaccines and subunit vaccines were associated with local adverse events and systemic events when compared with inactivated vaccines. Conclusion: Our study suggested that till date, COVID-19 vaccination is still a preferred pharmaceutical way to control the widespread pandemic. However, all reported adverse events should be revisited to provide further evidence for mass vaccinations.
Keywords: COVID-19; effectiveness; safety; umbrella meta-analysis; vaccination.
Copyright © 2023 Jiesisibieke, Liu, Yang, Chien and Tung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures
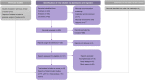

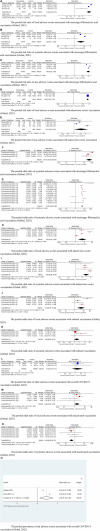
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed January 13, 2022).
-
- Fernandes N. Economic Effects of Coronavirus Outbreak (COVID-19) on the World Economy (2020). 10.2139/ssrn.3557504 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

