Endovascular and Percutaneous Embolotherapy for the Body and Extremity Arteriovenous Malformations
- PMID: 37485480
- PMCID: PMC10359173
- DOI: 10.22575/interventionalradiology.2022-0008
Endovascular and Percutaneous Embolotherapy for the Body and Extremity Arteriovenous Malformations
Abstract
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) consist of abnormal communications between the arteries and veins. They can involve any part of the body and extremity and grow in proportion to age and in response to hormonal influence or trauma. When symptoms progress from Schöbinger clinical stage II to III, transcatheter and/or direct puncture embolization are less-invasive and repeatable options for symptom palliation. The goal of embolization is to obliterate the AV shunt, and the choice of lesion access and embolic agents is based on the individual anatomy and flow. Embolization can be technically challenging due to complex vascular anatomy and morbidity risks. Therefore, a multidisciplinary management is essential for the diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of AVMs.
Keywords: arteriovenous fistula; arteriovenous malformations; arteriovenous shunt; embolic agents; embolization.
© 2023 Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None
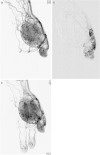
Figures


References
-
- Tasiou A, Tzerefos C, Alleyne CH Jr, et al. Arteriovenous malformations: congenital or acquired lesions? World Neurosurg. 2020; 134: e799-e807 - PubMed
-
- Greene AK, Liu AS, Mulliken JB, Chalache K, Fishman SJ. Vascular anomalies in 5621 patients: guidelines for referral. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46: 1784-1789. - PubMed
-
- Kohout MP, Hansen M, Pribaz JJ, Mulliken JB. Arteriovenous malformations of the head and neck: natural history and management. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 102: 643-654. - PubMed
-
- Liu AS, Mulliken JB, Zurakowski D, Fishman SJ, Greene AK. Extracranial arteriovenous malformations: natural progression and recurrence after treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 125: 1185-1194. - PubMed

