Bioorthogonal CRISPR/Cas9-Drug Conjugate: A Combinatorial Nanomedicine Platform
- PMID: 37485817
- PMCID: PMC10520654
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202302253
Bioorthogonal CRISPR/Cas9-Drug Conjugate: A Combinatorial Nanomedicine Platform
Abstract
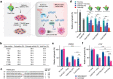
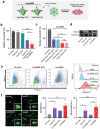
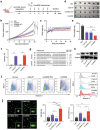
Bioconjugation of proteins can substantially expand the opportunities in biopharmaceutical development, however, applications are limited for the gene editing machinery despite its tremendous therapeutic potential. Here, a self-delivered nanomedicine platform based on bioorthogonal CRISPR/Cas9 conjugates, which can be armed with a chemotherapeutic drug for combinatorial therapy is introduced. It is demonstrated that multi-functionalized Cas9 with a drug and polymer can form self-condensed nanocomplexes, and induce significant gene editing upon delivery while avoiding the use of a conventional carrier formulation. It is shown that the nanomedicine platform can be applied for combinatorial therapy by incorporating the anti-cancer drug olaparib and targeting the RAD52 gene, leading to significant anti-tumor effects in BRCA-mutant cancer. The current development provides a versatile nanomedicine platform for combination treatment of human diseases such as cancer.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; bioorthogonal; cancer therapy; chemotherapeutic drugs; combinatorial delivery; gene editing; nanomedicines; unnatural amino acids.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Boutureira O., Bernardes G. J., Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2174. - PubMed
-
- Hoyt E. A., Cal P. M., Oliveira B. L., Bernardes G. J., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 147.
-
- Reguera L., Méndez Y., Humpierre A. R., Valdés O., Rivera D. G., Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1475. - PubMed
-
- Beck A., Goetsch L., Dumontet C., Corvaïa N., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2017, 16, 315. - PubMed
-
- Walsh S. J., Bargh J. D., Dannheim F. M., Hanby A. R., Seki H., Counsell A. J., Ou X., Fowler E., Ashman N., Takada Y., Isidro‐Llobet A., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
