Lipoblastoma Arising in the Head and Neck: A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 20 Cases
- PMID: 37486535
- PMCID: PMC10514009
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-023-01575-5
Lipoblastoma Arising in the Head and Neck: A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 20 Cases
Abstract
Background: Lipoblastomas (LPBs) are benign adipocytic neoplasms believed to recapitulate the development of embryonal fat.
Methods: We investigated the clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical features of 20 lipoblastomas arising in the head and neck in 18 patients.
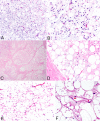
Results: Patients included 6 males and 12 females (1:2 ratio) with age at diagnosis ranging from 4 months to 28 years. Tumors occurred more commonly in the neck (12, 66.7%) and less commonly in the forehead, scalp, and tongue (2, 11.1%). Tumor size ranged from 1.4 to 6.0 cm (median 5.0 cm). Two patients, a 4-month-old female and 3-year-old male, had local recurrence of neck tumors at 4 months and 3 years after excision, respectively. Microscopically, tumors had a lobulated growth pattern and consisted of adipocytes at varying stages of differentiation. In addition to the classical histologic features, lipoma-like and myxoid variants constituted 45% of cases. Metaplastic elements, including brown fat and cartilage, were identified in two cases.
Conclusions: LPBs arising in the head and neck region are not uncommon and occurred at a rate of 9% in our cohort. They should be kept in the differential diagnosis when a fatty tumor is encountered in an older child or occurring at an unusual location.
Keywords: Lipoblast; Lipoblastoma; Lipoma; Neck; PLAG1.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- The WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . WHO classification of tumours soft tissue and bone tumours. 5. Lyon: IARC Press; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

