WNT ligands in non-small cell lung cancer: from pathogenesis to clinical practice
- PMID: 37486552
- PMCID: PMC10366069
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-023-00739-7
WNT ligands in non-small cell lung cancer: from pathogenesis to clinical practice
Abstract
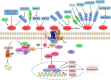
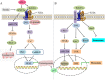
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and leading cause of death worldwide, whereas its pathogenesis has not been fully elucidated. Although mutations in some crucial genes in WNT pathways such as β-catenin and APC are not common in NSCLC, the abnormal signal transduction of WNT pathways is still closely related to the occurrence and progression of NSCLC. WNT ligands (WNTs) are a class of secreted glycoproteins that activate WNT pathways through binding to their receptors and play important regulatory roles in embryonic development, cell differentiation, and tissue regeneration. Therefore, the abnormal expression or dysfunction of WNTs undoubtedly affects WNT pathways and thus participates in the pathogenesis of diseases. There are 19 members of human WNTs, WNT1, WNT2, WNT2b, WNT3, WNT3a, WNT4, WNT5a, WNT5b, WNT6, WNT7a, WNT7b, WNT8a, WNT8b, WNT9a, WNT9b, WNT10a, WNT10b, WNT11 and WNT16. The expression levels of WNTs, binding receptors, and activated WNT pathways are diverse in different tissue types, which endows the complexity of WNT pathways and multifarious biological effects. Although abundant studies have reported the role of WNTs in the pathogenesis of NSCLC, it still needs further study as therapeutic targets for lung cancer. This review will systematically summarize current research on human WNTs in NSCLC, from molecular pathogenesis to potential clinical practice.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer; Therapeutic targets; WNT ligands; WNT signaling pathways.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, Carcereny E, Leighl NB, Ahn MJ, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with Advanced non–small-cell lung Cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518–27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00934. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 222102310174/Key Program for Science and Technology of Henan Province
- SBGJ202102214/Province and Ministry Co-construction Key Program for Medical Science and Technology of Henan Province
- 2203005/Key Program for Science and Technology of Kaifeng City
- 81700731/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 232300420048/Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
