Treatment Patterns and Healthcare Resource Utilization Among Newly Diagnosed Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Axial Spondyloarthritis, and Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients with Past Diagnosis of an Inflammatory Condition: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Claims Data in the United States
- PMID: 37486558
- PMCID: PMC10499741
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-023-02558-2
Treatment Patterns and Healthcare Resource Utilization Among Newly Diagnosed Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Axial Spondyloarthritis, and Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients with Past Diagnosis of an Inflammatory Condition: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Claims Data in the United States
Abstract
Introduction: Psoriasis (PSO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) are chronic inflammatory diseases (CIDs) often diagnosed and treated individually. However, genetic overlaps exist among CIDs, and patients with one are at risk of developing others within the same spectrum. This analysis characterized treatment patterns along with clinical and economic burdens of newly diagnosed CIDs among patients with an additional past diagnosis of PSO, PsA, axSpA, or HS.
Methods: This study used MarketScan® databases to examine demographics, treatment patterns, and healthcare resource utilization for patients with ≥ 1 claim for PSO or HS or ≥ 2 claims for PsA or axSpA, and continuous enrollment in the year before (baseline period) and following (follow-up period) the date of first diagnosis (incident diagnosis). Comorbidities and new CID diagnoses with a past diagnosis of PSO, PsA, axSpA, or HS, were examined.
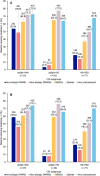
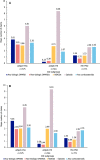
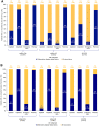
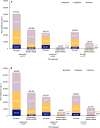
Results: The analysis included 298,794 patients (maximum of 1202 patients with ≥ 1 incident diagnoses): 134,233 had incident PSO; 9914 had incident PsA; 115,194 had incident axSpA; and 40,655 had incident HS. Prevalence of ≥ 1 CID diagnosis among patients with past diagnosis of PSO, PsA, axSpA, or HS was 4959/134,233 (3.7%), 5256/9914 (53.0%), 3205/115,194 (2.8%), and 1180/40,655 (2.9%), respectively. In patients with incident axSpA and past PsA diagnosis, incident axSpA and past HS diagnosis, and incident HS and past PSO diagnosis, steroid and opioid use were high across baseline and follow-up periods and use of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs increased from baseline to follow-up. Disease-related costs increased absolutely and increased or remained high as a proportion of all-cause costs.
Conclusion: Patients with newly diagnosed CIDs and additional past diagnosis of PSO, PsA, axSpA, or HS experienced high treatment utilization and healthcare costs. These findings highlight the need for payers, health technology assessment agencies, clinicians, and other stakeholders to explore the co-management of CIDs, rather than treating them separately.
Keywords: Axial spondyloarthritis; Hidradenitis suppurativa; Psoriasis; Psoriatic arthritis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Sari Hopson: Employee of Bristol Myers Squibb, former employee of UCB Pharma; Liza R. Gibbs, Sahar Syed: Employees and stockholders of Aetion, Inc; Robert Low, Laura McClung, Silky Beaty: Employees and stockholders of UCB Pharma.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong AW, Foster SA, Comer BS, et al. Real-world health outcomes in adults with moderate-to-severe psoriasis in the United States: a population study using electronic health records to examine patient-perceived treatment effectiveness, medication use, and healthcare resource utilization. BMC Dermatol. 2018;18(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12895-018-0072-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

