Simplified and highly-reliable automated production of [18F]FSPG for clinical studies
- PMID: 37486582
- PMCID: PMC10366059
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-023-00200-8
Simplified and highly-reliable automated production of [18F]FSPG for clinical studies
Abstract
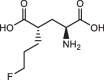
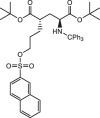
Background: (S)-4-(3-18F-Fluoropropyl)-L-Glutamic Acid ([18F]FSPG) is a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer that specifically targets the cystine/glutamate antiporter (xc-), which is frequently overexpressed in cancer and several neurological disorders. Pilot studies examining the dosimetry and biodistribution of [18F]FSPG in healthy volunteers and tumor detection in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and brain tumors showed promising results. In particular, low background uptake in the brain, lung, liver, and bowel was observed that further leads to excellent imaging contrasts of [18F]FSPG PET. However, reliable production-scale cGMP-compliant automated procedures for [18F]FSPG production are still lacking to further increase the utility and clinical adoption of this radiotracer. Herein, we report the optimized automated approaches to produce [18F]FSPG through two commercially available radiosynthesizers capable of supporting centralized and large-scale production for clinical use.
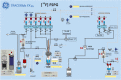
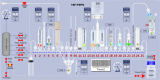
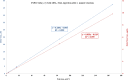
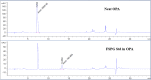
Results: Starting with activity levels of 60-85 GBq, the fully-automated process to produce [18F]FSPG took less than 45 min with average radiochemical yields of 22.56 ± 0.97% and 30.82 ± 1.60% (non-decay corrected) using TRACERlab™ FXFN and FASTlab™, respectively. The radiochemical purities were > 95% and the formulated [18F]FSPG solution was determined to be sterile and colorless with the pH of 6.5-7.5. No radiolysis of the product was observed up to 8 h after final batch formulation.
Conclusions: In summary, cGMP-compliant radiosyntheses and quality control of [18F]FSPG have been established on two commercially available synthesizers leveraging high activity concentration and radiochemical purity. While the clinical trials using [18F]FSPG PET are currently underway, the automated approaches reported herein will accelerate the clinical adoption of this radiotracer and warrant centralized and large-scale production of [18F]FSPG.
Keywords: Automation; PET; Radiopharmaceutical; [18F]FSPG.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Simplified and Highly-reliable automated production of [18F]FSPG for clinical studies.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 26:rs.3.rs-3031030. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3031030/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2023 Jul 24;8(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s41181-023-00200-8. PMID: 37461634 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Baek S, Choi CM, Ahn SH, Lee JW, Gong G, Ryu JS, Oh SJ, Bacher-Stier C, Fels L, Koglin N, Hultsch C, Schatz CA, Dinkelborg LM, Mittra ES, Gambhir SS, Moon DH. Exploratory clinical trial of (4s)-4-(3-[18f]Fluoropropyl)-L-Glutamate for imaging Xc− transporter using positron emission tomography in patients with non-small cell lung or breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:5427–5437. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0214. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carbone M, Harbour JW, Brugarolas J, Bononi A, Pagano I, Dey A, Krausz T, Pass HI, Yang H, Gaudino G. Biological mechanisms and clinical significance of Bap1 mutations in human cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:1103–1120. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1220. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
