A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 37487152
- PMCID: PMC10870872
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202303-0558WS
A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
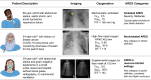
Background: Since publication of the 2012 Berlin definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), several developments have supported the need for an expansion of the definition, including the use of high-flow nasal oxygen, the expansion of the use of pulse oximetry in place of arterial blood gases, the use of ultrasound for chest imaging, and the need for applicability in resource-limited settings. Methods: A consensus conference of 32 critical care ARDS experts was convened, had six virtual meetings (June 2021 to March 2022), and subsequently obtained input from members of several critical care societies. The goal was to develop a definition that would 1) identify patients with the currently accepted conceptual framework for ARDS, 2) facilitate rapid ARDS diagnosis for clinical care and research, 3) be applicable in resource-limited settings, 4) be useful for testing specific therapies, and 5) be practical for communication to patients and caregivers. Results: The committee made four main recommendations: 1) include high-flow nasal oxygen with a minimum flow rate of ⩾30 L/min; 2) use PaO2:FiO2 ⩽ 300 mm Hg or oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry SpO2:FiO2 ⩽ 315 (if oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry is ⩽97%) to identify hypoxemia; 3) retain bilateral opacities for imaging criteria but add ultrasound as an imaging modality, especially in resource-limited areas; and 4) in resource-limited settings, do not require positive end-expiratory pressure, oxygen flow rate, or specific respiratory support devices. Conclusions: We propose a new global definition of ARDS that builds on the Berlin definition. The recommendations also identify areas for future research, including the need for prospective assessments of the feasibility, reliability, and prognostic validity of the proposed global definition.
Keywords: ARDS; acute lung injury; pulmonary edema.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Ready for Prime Time?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Jan 1;209(1):14-16. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202308-1369ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 37677146 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
From Berlin to Global: The Need for Syndromic Definitions of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Jan 1;209(1):21-23. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202308-1441VP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 37816094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pitfalls of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Diagnosis Based on Interventions.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 May 15;209(10):1278-1279. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202308-1368LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38507733 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
"PEEP-adjusted P/F Ratio" in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Call for Further Enhancement of Global Definition.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 May 15;209(10):1279-1280. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202308-1428LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38507734 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL, Levine BE. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet . 1967;2:319–323.
-
- Murray JF, Matthay MA, Luce JM, Flick MR. An expanded definition of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis . 1988;138:720–723. - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, et al. The Consensus Committee Report of the American-European consensus conference on ARDS: definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes and clinical trial coordination. Intensive Care Med . 1994;20:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, Fan E, et al. ARDS Definition Task Force Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA . 2012;307:2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson ND, Fan E, Camporota L, Antonelli M, Anzueto A, Beale R, et al. The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material. Intensive Care Med . 2012;38:1573–1582. - PubMed

