m5C regulator-mediated methylation modification phenotypes characterized by distinct tumor microenvironment immune heterogenicity in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 37488178
- PMCID: PMC10366215
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37300-z
m5C regulator-mediated methylation modification phenotypes characterized by distinct tumor microenvironment immune heterogenicity in colorectal cancer
Abstract
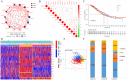
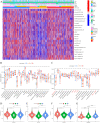
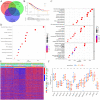
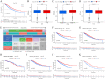
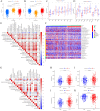
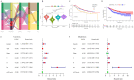
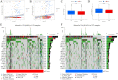
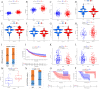
The RNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification has been demonstrated to be an important epigenetic regulator and to impact colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. However, the potential roles of m5C modification in immune cell infiltration in the CRC tumor microenvironment (TME) remain unknown. The m5C modification phenotypes were comprehensively evaluated based on 14 m5C regulators in a meta-CRC cohort of 1792 patients and systematically correlated with the m5C modification phenotypes, immune cell infiltration characteristics and known biological processes. The m5Cscore model was constructed by principal component analysis (PCA) algorithms to quantify the m5C modification phenotypes of individual CRC samples and was used to predict the immunotherapy response. We identified three m5C modification phenotypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes and biological processes among the 1792 meta-CRC patients. Three phenotypes with a highly consistent TME landscape and characteristics were revealed: immune excluded, immune desert and immune inflammation. The meta-CRC patients were divided into high and low m5Cscore subgroups based on the m5Cscore. The m5Cscore was confirmed to have a negative correlation with infiltrating immune cells and PD-L1 expression and a positive correlation with tumor mutation burden (TMB), mutation rate and microsatellite instability (MSI) score. Moreover, patients in the low m5Cscore group had better immunotherapy responses and significant durable survival benefits in independent anti-PD-1/L1 immunotherapy cohorts for the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapeutic strategy. This study revealed that m5C modification plays a crucial role in TME composition and complexity. Comprehensive evaluation of the m5C modification phenotypes of individual patients will enhance our understanding of TME characteristics and promote the application of more appropriate and personalized treatment strategies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pietro B, Filip S, Angana R, et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;2022(50):231–235. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1083. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

