A female of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 caused by heterozygous mutations of ABCB4 gene and her cirrhosis improved after treatment of ursodeoxycholic acid: a case report
- PMID: 37488596
- PMCID: PMC10367406
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01602-y
A female of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 caused by heterozygous mutations of ABCB4 gene and her cirrhosis improved after treatment of ursodeoxycholic acid: a case report
Abstract
Background: Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of rapidly progressive autosomal recessive disorders characterized by intrahepatic cholestasis. PFIC-3 is caused by mutations in the ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 gene (ABCB4), which encodes multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3/ABCB4). Patients are usually in infancy or childhood, but cirrhosis and portal hypertension may be the first manifestation in older children or young adults.
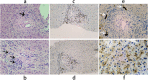
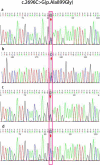
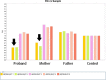
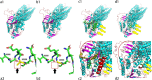
Case presentation: A 25-year-old young woman with recurrent abnormal hepatic function was mainly characterized by increased gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and bile acid with cryptogenic cirrhosis. After 7 months of treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), her hepatic pathology suggested there were also obvious widening and venous fibrosis around the portal vein, and slight bile duct hyperplasia at the edge of the portal area. Infiltration of inflammatory cells around the portal vein and hepatocyte ABCB4/MDR3 protein was basically normal. Sequencing indicated the patient had heterozygous mutations in the ABCB4 gene: c.2696C > G and wes [hg19]7q21.12(87032513-87033422) × 1. Through SWISS-MODEL Predict for protein structures, the missense mutation results in protein side chain missing a methyl group (-CH3), and the deletion mutation results in the serious damage to the structure of MDR3 protein which lead to phosphatidylcholine deficiency of bile in the capillary bile ducts. The toxic effect of bile salts then damages the bile ducts, causing cholestasis and cholangitis, which can then develop into biliary cirrhosis. Through the analysis of pathogenicity prediction software, the mutations led to PFIC3. After treatment of UDCA for 29 months, her cirrhosis was improved, hepatic function was close to normal.
Conclusion: Novel heterozygous mutations are the molecular pathological cause of PFIC3 in this patient. All young adult patients with occult cirrhosis should be tested for ABCB4. Early diagnosis of PFIC3 and continued treatment with UDCA are key to improving prognosis and delaying the onset of end-stage liver disease.
Keywords: ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 4 (ABCB4) gene; Case report; Multidrug-resistant protein 3 (MDR3); Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3); Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

