Ethanol changes Nestin-promoter induced neural stem cells to disturb newborn dendritic spine remodeling in the hippocampus of mice
- PMID: 37488906
- PMCID: PMC10503613
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.379051
Ethanol changes Nestin-promoter induced neural stem cells to disturb newborn dendritic spine remodeling in the hippocampus of mice
Abstract
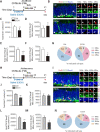
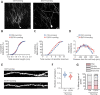
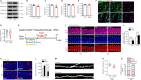
Adolescent binge drinking leads to long-lasting disorders of the adult central nervous system, particularly aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis. In this study, we applied in vivo fluorescent tracing using NestinCreERT2::Rosa26-tdTomato mice and analyzed the endogenous neurogenesis lineage progression of neural stem cells (NSCs) and dendritic spine formation of newborn neurons in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus. We found abnormal orientation of tamoxifen-induced tdTomato+ (tdTom+) NSCs in adult mice 2 months after treatment with EtOH (5.0 g/kg, i.p.) for 7 consecutive days. EtOH markedly inhibited tdTom+ NSCs activation and hippocampal neurogenesis in mouse dentate gyrus from adolescence to adulthood. EtOH (100 mM) also significantly inhibited the proliferation to 39.2% and differentiation of primary NSCs in vitro. Adult mice exposed to EtOH also exhibited marked inhibitions in dendritic spine growth and newborn neuron maturation in the dentate gyrus, which was partially reversed by voluntary running or inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin-enhancer of zeste homolog 2 pathway. In vivo tracing revealed that EtOH induced abnormal orientation of tdTom+ NSCs and spatial misposition defects of newborn neurons, thus causing the disturbance of hippocampal neurogenesis and dendritic spine remodeling in mice.
Keywords: EZH2; adolescence; adulthood; dentate gyrus; ethanol; in vivo; lineage progression; mTOR; neural stem cell; newborn dendritic spine; newborn neurons; tracing.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resistance of Postnatal Hippocampal Neurogenesis to Alcohol Toxicity in a Third Trimester-Equivalent Mouse Model of Gestational Alcohol Exposure.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Dec;43(12):2504-2513. doi: 10.1111/acer.14207. Epub 2019 Oct 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31573091 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenic deficits in HIV-1 Tg26 transgenic mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Oct 12;15(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1322-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30314515 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Neural Circuit Formation in a Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis Mouse Model.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 8;40(2):447-458. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0866-19.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31719166 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus.Anat Histol Embryol. 2020 Jan;49(1):3-16. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12496. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020. PMID: 31568602 Review.
-
Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus: history, regulation, and prospective roles.Int J Neurosci. 2019 Jun;129(6):598-611. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2018.1545771. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Int J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30433866 Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution, contribution and regulation of nestin+ cells.J Adv Res. 2024 Jul;61:47-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.08.013. Epub 2023 Aug 28. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37648021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2-dependent myelination following sciatic nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Aug 1;20(8):2382-2394. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-02040. Epub 2024 May 13. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39359095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaux-Cantin S, Warnault V, Legastelois R, Botia B, Pierrefiche O, Vilpoux C, Naassila M. Alcohol intoxications during adolescence increase motivation for alcohol in adult rats and induce neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology. (2013);67:521–531. - PubMed
-
- Bartels C, Kunert HJ, Stawicki S, Kroner-Herwig B, Ehrenreich H, Krampe H. Recovery of hippocampus-related functions in chronic alcoholics during monitored long-term abstinence. Alcohol Alcohol. (2007);42:92–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

