Discovery of novel arylamide derivatives containing piperazine moiety as inhibitors of tubulin polymerisation with potent liver cancer inhibitory activity
- PMID: 37489043
- PMCID: PMC10392279
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2237701
Discovery of novel arylamide derivatives containing piperazine moiety as inhibitors of tubulin polymerisation with potent liver cancer inhibitory activity
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2255447. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2255447. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37667497 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
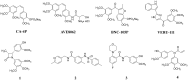
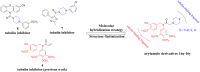
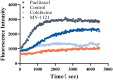
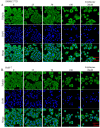
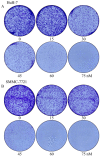
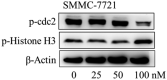
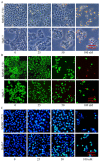
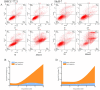
In this work, a series of novel arylamide derivatives containing piperazine moiety were designed and synthesised as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors. Among 25 target compounds, compound 16f (MY-1121) exhibited low nanomolar IC50 values ranging from 0.089 to 0.238 μM against nine human cancer cells. Its inhibitory effects on liver cancer cells were particularly evident with IC50 values of 89.42 and 91.62 nM for SMMC-7721 and HuH-7 cells, respectively. Further mechanism studies demonstrated that compound 16f (MY-1121) could bind to the colchicine binding site of β-tubulin and directly act on β-tubulin, thus inhibiting tubulin polymerisation. Additionally, compound 16f (MY-1121) could inhibit colony forming ability, cause morphological changes, block cell cycle arrest at the G2 phase, induce cell apoptosis, and regulate the expression of cell cycle and cell apoptosis related proteins in liver cancer cells. Overall, the promising bioactivities of compound 16f (MY-1121) make the novel arylamide derivatives have the value for further development as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors with potent anticancer activities.
Keywords: Tubulin; antiproliferative activities; arylamide; piperazine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there was no conflict of interest about this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Shuai W, Wang G, Zhang Y, Bu F, Zhang S, Miller DD, Li W, Ouyang L, Wang Y.. Recent progress on tubulin inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 2021;64(12):7963–7990. - PubMed
-
- Kavallaris M. Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(3):194–204. - PubMed
-
- Mosca L, Ilari A, Fazi F, Assaraf YG, Colotti G.. Taxanes in cancer treatment: activity, chemoresistance and its overcoming. Drug Resist Updat. 2021;54:100742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
