Label-free discrimination of extracellular vesicles from large lipoproteins
- PMID: 37489102
- PMCID: PMC10366660
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12348
Label-free discrimination of extracellular vesicles from large lipoproteins
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are increasingly gaining interest as biomarkers and therapeutics. Accurate sizing and quantification of EVs remain problematic, given their nanometre size range and small scattering cross-sections. This is compounded by the fact that common EV isolation methods result in co-isolation of particles with comparable features. Especially in blood plasma, similarly-sized lipoproteins outnumber EVs to a great extent. Recently, interferometric nanoparticle tracking analysis (iNTA) was introduced as a particle analysis method that enables determining the size and refractive index of nanoparticles with high sensitivity and precision. In this work, we apply iNTA to differentiate between EVs and lipoproteins, and compare its performance to conventional nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). We show that iNTA can accurately quantify EVs in artificial EV-lipoprotein mixtures and in plasma-derived EV samples of varying complexity. Conventional NTA could not report on EV numbers, as it was not able to distinguish EVs from lipoproteins. iNTA has the potential to become a new standard for label-free EV characterization in suspension.
Keywords: concentration; extracellular vesicles; interferometric scattering; lipoproteins; plasma; refractive index; size.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D.K., M.B., and V.S. have filed an International Patent Application (PCT) based on this work in the name of the Max Planck Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e.V. J.V.D. is listed as co‐inventor on a patent concerning dual‐mode chromatography (US20230070693). The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
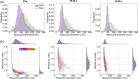
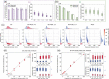


Similar articles
-
Physical association of low density lipoprotein particles and extracellular vesicles unveiled by single particle analysis.J Extracell Vesicles. 2023 Nov;12(11):e12376. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12376. J Extracell Vesicles. 2023. PMID: 37942918 Free PMC article.
-
Preanalytical, analytical, and biological variation of blood plasma submicron particle levels measured with nanoparticle tracking analysis and tunable resistive pulse sensing.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2016 Sep;76(5):349-60. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2016.1178801. Epub 2016 May 19. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27195974
-
Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid and Plasma of Patients with Lung Lesions Using Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis.Cells. 2021 Dec 9;10(12):3473. doi: 10.3390/cells10123473. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943982 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: An Effective Tool to Characterize Extracellular Vesicles.Molecules. 2024 Oct 1;29(19):4672. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194672. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Nanoparticles - Influence on Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Characterization.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 10;12:773844. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.773844. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867406 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an easy non-destructive particle isolation protocol for quality control of red blood cell concentrates.J Extracell Biol. 2025 Jan 17;4(1):e70028. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70028. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Extracell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39830833 Free PMC article.
-
Label-Free Anti-Brownian Trapping of Single Nanoparticles in Solution.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024 Nov 19;128(47):20275-20286. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c05878. eCollection 2024 Nov 28. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39634022 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal CD40, CD25, and Serum CA19-9 as Combinatory Novel Liquid Biopsy Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 11;26(4):1500. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041500. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003965 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Angle Interferometric Scattering Microscopy for Optical Multiparametric Particle Characterization.Nano Lett. 2024 Feb 14;24(6):1874-1881. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03539. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Nano Lett. 2024. PMID: 38295760 Free PMC article.
-
An Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Paper Strip for Rapid and Convenient Estimation of EV Concentration.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 May 6;15(5):294. doi: 10.3390/bios15050294. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan, D. B. , Caswell, T. , Keim, N. C. , van der Wel, C. M. , & Verweij, R. W. (2021). soft‐matter/trackpy: Trackpy v0.5.0.
-
- Arab, T. , Mallick, E. R. , Huang, Y. , Dong, L. , Liao, Z. , Zhao, Z. , Gololobova, O. , Smith, B. , Haughey, N. J. , Pienta, K. J. , Slusher, B. S. , Tarwater, P. M. , Tosar, J. P. , Zivkovic, A. M. , Vreeland, W. N. , Paulaitis, M. E. , & Witwer, K. W. (2021). Characterization of extracellular vesicles and synthetic nanoparticles with four orthogonal single‐particle analysis platforms. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 10(6), e12079. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai, K. , Barnett, G. V. , Kar, S. R. , & Das, T. K. (2017). Interference from proteins and surfactants on particle size distributions measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Pharmaceutical Research, 34, 800–808. - PubMed
-
- Breiman, L. (2001). Mach. Learn, 45, 5–32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

