Complex Neuroimmune Involvement in Neurodevelopment: A Mini-Review
- PMID: 37489149
- PMCID: PMC10363380
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S410562
Complex Neuroimmune Involvement in Neurodevelopment: A Mini-Review
Abstract
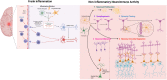
It is increasingly evident that cells and molecules of the immune system play significant roles in neurodevelopment. As perinatal infection is associated with the development of neurodevelopmental disorders, previous research has focused on demonstrating that the induction of neuroinflammation in the developing brain is capable of causing neuropathology and behavioral changes. Recent studies, however, have revealed that immune cells and molecules in the brain can influence neurodevelopment without the induction of overt inflammation, identifying neuroimmune activities as integral parts of normal neurodevelopment. This mini-review describes the shift in literature that has moved from emphasizing the intrusion of inflammatory events as a main culprit of neurodevelopmental disorders to evaluating the deviation of the normal neuroimmune activities in neurodevelopment as a potential pathogenic mechanism.
Keywords: cytokine; glia; neurodevelopmental disorders; neuroinflammation.
© 2023 Monet and Quan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

