mmu-miRNA-342-3p promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis induced by Echinococcus multilocularis infection via targeting Zbtb7a
- PMID: 37490505
- PMCID: PMC10403128
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011520
mmu-miRNA-342-3p promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis induced by Echinococcus multilocularis infection via targeting Zbtb7a
Abstract
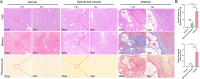
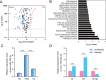
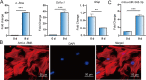
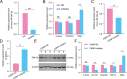
Liver fibrosis is one of the histopathological characters during Echinococcus multilocularis infection. The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is a key event in the development of liver fibrosis. However, the molecular mechanism of HSC activation in the E. multilocularis infection-induced liver fibrosis remains largely unclear. Here, we reported that mmu-miR-342-3p was most dominantly expressed in HSCs and was upregulated in the HSCs in response to E. multilocularis infection. We further showed that mmu-miR-342-3p was able to bind to the 3' UTR of the Zbtb7a gene and regulated its expression. Moreover, mmu-miR-342-3p expression was negatively correlated with its target gene Zbtb7a in HSCs during E. multilocularis infection. Knockdown of mmu-miR-342-3p promoted the expression of Gfap in the activated HSCs in vitro. In the E. multilocularis-infected mice, knockdown of mmu-miR-342-3p suppressed the expression of α-Sma, Col1α1, and TGF-β but promoted the expression of Gfap. Therefore, mmu-miR-342-3p is a key regulator for activation of HSCs, and inhibiting mmu-miR-342-3p to suppressed Zbtb7a-mediated TGF-β signaling in activated HSCs could be a novel strategy to treat liver fibrosis induced by E. multilocularis.
Copyright: © 2023 Cao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-142-3p blocks TGF-β-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells through targeting TGFβRI.Life Sci. 2017 Oct 15;187:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28823564
-
miR-140-3p Knockdown Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Fibrogenesis in Hepatic Stellate Cells via PTEN-Mediated AKT/mTOR Signaling.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Jun;60(6):561-569. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.561. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 31124340 Free PMC article.
-
miR-193a/b-3p relieves hepatic fibrosis and restrains proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):3824-3832. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14210. Epub 2019 Apr 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30945448 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA gm40262 promotes liver fibrosis and parasite growth through the gm40262-miR-193b-5p-TLR4/Col1α1 axis.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0228724. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02287-24. Epub 2025 Feb 25. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39998227 Free PMC article.
-
Twist1-induced miR-199a-3p promotes liver fibrosis by suppressing caveolin-2 and activating TGF-β pathway.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 5;5(1):75. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0169-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32499481 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MIAT promotes myofibroblastic activities and transformation in oral submucous fibrosis through sponging the miR-342-3p/SOX6 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Oct 7;16(19):12909-12927. doi: 10.18632/aging.206121. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39379100 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential miRNA biomarkers for neurobrucellosis diagnosis.Front Physiol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1463597. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1463597. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40626048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casulli A, Barth TFE, Tamarozzi F. Echinococcus multilocularis. Trends Parasitol. 2019; 35:738–739. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

