Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer
- PMID: 37491279
- PMCID: PMC10367370
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-023-01478-6
Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer
Abstract
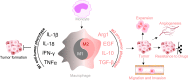
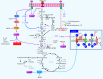
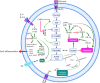
Tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) are crucial components of the tumour microenvironment and play a significant role in tumour development and drug resistance by creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Macrophages are essential components of both the innate and adaptive immune systems and contribute to pathogen resistance and the regulation of organism homeostasis. Macrophage function and polarization are closely linked to altered metabolism. Generally, M1 macrophages rely primarily on aerobic glycolysis, whereas M2 macrophages depend on oxidative metabolism. Metabolic studies have revealed that the metabolic signature of TAMs and metabolites in the tumour microenvironment regulate the function and polarization of TAMs. However, the precise effects of metabolic reprogramming on tumours and TAMs remain incompletely understood. In this review, we discuss the impact of metabolic pathways on macrophage function and polarization as well as potential strategies for reprogramming macrophage metabolism in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; Metabolism; Metabolism reprogramming; Tumour microenvironment; Tumour-associated macrophages.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of intrinsic and extrinsic metabolic pathways in tumour-associated macrophages.FEBS J. 2023 Jun;290(12):3040-3058. doi: 10.1111/febs.16465. Epub 2022 May 7. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 35486022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage Polarisation in the Tumour Microenvironment: Recent Research Advances and Therapeutic Potential of Different Macrophage Reprogramming.Cancer Control. 2025 Jan-Dec;32:10732748251316604. doi: 10.1177/10732748251316604. Cancer Control. 2025. PMID: 39849988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages in shaping the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114504. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114504. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37002579 Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming in the immunosuppression of tumor-associated macrophages.Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Oct 20;135(20):2405-2416. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002426. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 36385099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lipid metabolism of macrophages: A new strategy for tumor therapy.J Adv Res. 2025 Feb;68:99-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.02.009. Epub 2024 Feb 18. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38373649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunonutrition, Metabolism, and Programmed Cell Death in Lung Cancer: Translating Bench to Bedside.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;13(6):409. doi: 10.3390/biology13060409. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating thyroid cancer complexity: the emerging role of EV-derived non-coding RNAs.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 4;11(1):142. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02411-1. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40185719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in the tumor immune microenvironment: a key force in combination therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1436174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436174. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39315102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting myeloid cells for hematological malignancies: the present and future.Biomark Res. 2025 Apr 10;13(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00775-1. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40205623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the eEF1A1/ARID3A/PKC-δ Complex by Neferine Inhibits Macrophage Glycolytic Reprogramming in Atherosclerosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(15):e2416158. doi: 10.1002/advs.202416158. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39973763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

