Access to Pediatric Neurology Training and Services Worldwide: A Survey by the International Child Neurology Association
- PMID: 37491325
- PMCID: PMC10634651
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207633
Access to Pediatric Neurology Training and Services Worldwide: A Survey by the International Child Neurology Association
Erratum in
-
Access to Pediatric Neurology Training and Services Worldwide: A Survey by the International Child Neurology Association.Neurology. 2024 Mar 12;102(5):e208125. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000208125. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 38315962 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
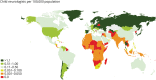
Pediatric neurology is the medical subspecialty responsible for diagnosing and managing diseases and disorders of the nervous system in childhood and adolescence. In many, but not all, regions of the world, the discipline of pediatric neurology is recognized as a specialty or subspecialty of either neurology or pediatrics. Significant knowledge and competencies in this area are necessary to be effective in clinical practice. The need for this is driven by the high burden of disease from neurologic conditions in children and the effect on their families. As the first part of a multistaged project under the auspices of the International Child Neurology Association, in collaboration with key stakeholders, a survey was undertaken to establish which countries have practicing child neurologists. For those countries that have child neurologists, the survey established the number of practitioners and which countries have access to in-country child neurology training. Responses were obtained from 177 countries. Worldwide, there is a median of 0.07 and mean of 0.39 child neurologists per 100,000 population. The greatest deficits in child neurology specialists and access to training were evident in countries which fell under the World Bank rating of low-income country status (range of 0-0.008 child neurologists per 100,000 population). Seventy-three percent of low-income countries lack access to child neurologists: The majority are in the African and South-East Asia regions. For the population of 1.37 billion in the continent of Africa, there were 324 child neurologists, equating to a median of 0.01 per 100,000 population in comparison with a median of 0.59 child neurologists per 100,000 across high-income countries. Ninety-four countries had capacity to support in-country pediatric neurology training. Worldwide, there are inadequate numbers of child neurologists and a great need for increased training capacity.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
J.M. Wilmshurst serves on the advisory board for the South African branch of Novartis and Sanofi. Honoraria received for work as associate editor for Epilepsia and chief editor for the pediatric neurology subsection of Frontiers in Neurology. C. Catsman-Berrevoets reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. D.L. Gilbert reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. L. Nagarajan received Honoraria from UCB, Novartis, and Biogen. P. Samia reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. E. Serdaroglu reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. C. Triki reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J. Vidaurre reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. B. Hameed reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Go to
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Atlas: Country Resources for Neurological Disorders. Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse, World Federation of Neurology; 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
