Differential CaKAN3-CaHSF8 associations underlie distinct immune and heat responses under high temperature and high humidity conditions
- PMID: 37491353
- PMCID: PMC10368638
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40251-8
Differential CaKAN3-CaHSF8 associations underlie distinct immune and heat responses under high temperature and high humidity conditions
Abstract
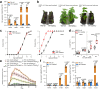
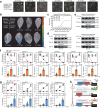
High temperature and high humidity (HTHH) conditions increase plant susceptibility to a variety of diseases, including bacterial wilt in solanaceous plants. Some solanaceous plant cultivars have evolved mechanisms to activate HTHH-specific immunity to cope with bacterial wilt disease. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we find that CaKAN3 and CaHSF8 upregulate and physically interact with each other in nuclei under HTHH conditions without inoculation or early after inoculation with R. solanacearum in pepper. Consequently, CaKAN3 and CaHSF8 synergistically confer immunity against R. solanacearum via activating a subset of NLRs which initiates immune signaling upon perception of unidentified pathogen effectors. Intriguingly, when HTHH conditions are prolonged without pathogen attack or the temperature goes higher, CaHSF8 no longer interacts with CaKAN3. Instead, it directly upregulates a subset of HSP genes thus activating thermotolerance. Our findings highlight mechanisms controlling context-specific activation of high-temperature-specific pepper immunity and thermotolerance mediated by differential CaKAN3-CaHSF8 associations.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression and functional evaluation of CaZNF830 during pepper response to Ralstonia solanacearum or high temperature and humidity.Microb Pathog. 2018 May;118:336-346. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.044. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29614367
-
MADS-box protein AGL8 interacts with chromatin-remodelling component SWC4 to activate thermotolerance and environment-dependent immunity in pepper.J Exp Bot. 2023 Jun 27;74(12):3667-3683. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad092. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36912616
-
Capsicum annuum HsfB2a Positively Regulates the Response to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection or High Temperature and High Humidity Forming Transcriptional Cascade with CaWRKY6 and CaWRKY40.Plant Cell Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;59(12):2608-2623. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcy181. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30169791
-
Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Sep;14(7):651-62. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12038. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23718203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAL effectors--pathogen strategies and plant resistance engineering.New Phytol. 2014 Dec;204(4):823-32. doi: 10.1111/nph.13015. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 25539004 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat Stress and Plant-Biotic Interactions: Advances and Perspectives.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;13(15):2022. doi: 10.3390/plants13152022. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Catalase Gene Family and the Function of SmCAT4 in Eggplant Response to Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16979. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316979. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069301 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies to improve heat stress tolerance in crops.aBIOTECH. 2025 Jan 24;6(1):97-115. doi: 10.1007/s42994-024-00195-z. eCollection 2025 Mar. aBIOTECH. 2025. PMID: 40060179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular identification and functional characterization of a transcription factor GeRAV1 from Gelsemium elegans.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09919-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38166591 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling the Bioactive Compounds in Broccoli Heads with Varying Organ Sizes and Growing Seasons.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 11;13(10):1329. doi: 10.3390/plants13101329. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

