Automated detection of intracranial aneurysms using skeleton-based 3D patches, semantic segmentation, and auxiliary classification for overcoming data imbalance in brain TOF-MRA
- PMID: 37491504
- PMCID: PMC10368697
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38586-9
Automated detection of intracranial aneurysms using skeleton-based 3D patches, semantic segmentation, and auxiliary classification for overcoming data imbalance in brain TOF-MRA
Abstract
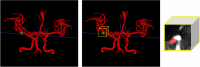
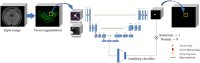
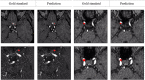
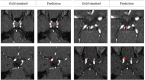
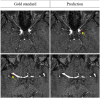
Accurate and reliable detection of intracranial aneurysms is vital for subsequent treatment to prevent bleeding. However, the detection of intracranial aneurysms can be time-consuming and even challenging, and there is great variability among experts, especially in the case of small aneurysms. This study aimed to detect intracranial aneurysms accurately using a convolutional neural network (CNN) with 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA). A total of 154 3D TOF-MRA datasets with intracranial aneurysms were acquired, and the gold standards were manually drawn by neuroradiologists. We also obtained 113 subjects from a public dataset for external validation. These angiograms were pre-processed by using skull-stripping, signal intensity normalization, and N4 bias correction. The 3D patches along the vessel skeleton from MRA were extracted. Values of the ratio between the aneurysmal and the normal patches ranged from 1:1 to 1:5. The semantic segmentation on intracranial aneurysms was trained using a 3D U-Net with an auxiliary classifier to overcome the imbalance in patches. The proposed method achieved an accuracy of 0.910 in internal validation and external validation accuracy of 0.883 with a 2:1 ratio of normal to aneurysmal patches. This multi-task learning method showed that the aneurysm segmentation performance was sufficient to be helpful in an actual clinical setting.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

