A Novel Classification Model Using Optimal Long Short-Term Memory for Classification of COVID-19 from CT Images
- PMID: 37491543
- PMCID: PMC10584759
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-023-00852-7
A Novel Classification Model Using Optimal Long Short-Term Memory for Classification of COVID-19 from CT Images
Abstract
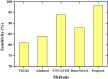
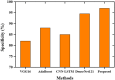
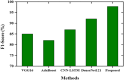
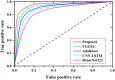
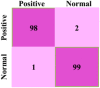
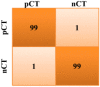
The human respiratory system is affected when an individual is infected with COVID-19, which became a global pandemic in 2020 and affected millions of people worldwide. However, accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 can be challenging due to small variations in typical and COVID-19 pneumonia, as well as the complexities involved in classifying infection regions. Currently, various deep learning (DL)-based methods are being introduced for the automatic detection of COVID-19 using computerized tomography (CT) scan images. In this paper, we propose the pelican optimization algorithm-based long short-term memory (POA-LSTM) method for classifying coronavirus using CT scan images. The data preprocessing technique is used to convert raw image data into a suitable format for subsequent steps. Here, we develop a general framework called no new U-Net (nnU-Net) for region of interest (ROI) segmentation in medical images. We apply a set of heuristic guidelines derived from the domain to systematically optimize the ROI segmentation task, which represents the dataset's key properties. Furthermore, high-resolution net (HRNet) is a standard neural network design developed for feature extraction. HRNet chooses the top-down strategy over the bottom-up method after considering the two options. It first detects the subject, generates a bounding box around the object and then estimates the relevant feature. The POA is used to minimize the subjective influence of manually selected parameters and enhance the LSTM's parameters. Thus, the POA-LSTM is used for the classification process, achieving higher performance for each performance metric such as accuracy, sensitivity, F1-score, precision, and specificity of 99%, 98.67%, 98.88%, 98.72%, and 98.43%, respectively.
Keywords: Computerized tomography scan images; Coronavirus; Disease prediction; High-resolution net; No new U-Net; Pelican optimization algorithm.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
COVID-DAI: A novel framework for COVID-19 detection and infection growth estimation using computed tomography images.Microsc Res Tech. 2022 Jun;85(6):2313-2330. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24088. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microsc Res Tech. 2022. PMID: 35194866 Free PMC article.
-
A novel adaptive cubic quasi-Newton optimizer for deep learning based medical image analysis tasks, validated on detection of COVID-19 and segmentation for COVID-19 lung infection, liver tumor, and optic disc/cup.Med Phys. 2023 Mar;50(3):1528-1538. doi: 10.1002/mp.15969. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36057788 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 lung CT image segmentation using deep learning methods: U-Net versus SegNet.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Feb 9;21(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12880-020-00529-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33557772 Free PMC article.
-
CAD systems for COVID-19 diagnosis and disease stage classification by segmentation of infected regions from CT images.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Jul 6;23(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04818-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35794537 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis using state-of-the-art CNN architecture features and Bayesian Optimization.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Mar;142:105244. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105244. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35077936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

