Ten-year follow-up report and neurologic sequelae in a case of neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism
- PMID: 37492070
- PMCID: PMC10363849
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.7626
Ten-year follow-up report and neurologic sequelae in a case of neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism
Abstract
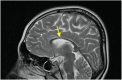
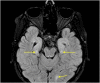
We present a 10-year follow-up and describe our experience in managing a case of neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT) for the first time in Iran. Microcephaly, mental retardation, and epilepsy may be long time sequels of NSHPT. The brain MRI findings are compatible with an old hypoxic-ischemic event.
Keywords: epilepsy; mental retardation; microcephaly; neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Perinatal asphyxia, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and neurological sequelae in full-term newborns. II. Description and interrelation].Rev Neurol. 1996 Aug;24(132):969-76. Rev Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8755359 Spanish.
-
Neonatal Severe Hyperparathyroidism: Novel Insights From Calcium, PTH, and the CASR Gene.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Apr 1;105(4):1061-78. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgz233. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31778168 Free PMC article.
-
Subtotal Parathyroidectomy Successfully Controls Calcium Levels of Patients with Neonatal Severe Hyperparathyroidism Carrying a Novel CASR Mutation.Horm Res Paediatr. 2023;96(4):432-438. doi: 10.1159/000528568. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Horm Res Paediatr. 2023. PMID: 36626889
-
Cinacalcet monotherapy in neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism: a case study and review.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jan;99(1):7-11. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2834. Epub 2013 Dec 20. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24203066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cinacalcet therapy in an infant with an R185Q calcium-sensing receptor mutation causing hyperparathyroidism: a case report and review of the literature.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Mar 26;32(3):305-310. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0307. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30730839 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources