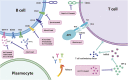
Advances in natural products and antibody drugs for SLE: new therapeutic ideas
- PMID: 37492083
- PMCID: PMC10363611
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1235440
Advances in natural products and antibody drugs for SLE: new therapeutic ideas
Abstract
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune systemic disease with a wide range of clinical symptoms, complex development processes, and uncertain prognosis. The clinical treatment of SLE is mainly based on hormones and immunosuppressants. Research on novel therapy strategies for SLE has flourished in recent years, especially the emergence of new targeted drugs and natural products that can modulate related symptoms. This review discusses the current experience including B-cell targeted drugs (belimumab, tabalumab, blisibimod, atacicept, rituximab, ofatumumab, ocrelizumab, obexelimab, and epratuzumab), T-cell targeted drugs (abatacept, dapirolizumab, and inhibitor of syk and CaMKIV), cytokines targeted drugs (anifrolumab and sifalimumab), and natural products (curcumin, oleuropein, punicalagin, sulforaphane, icariin, apigenin, and resveratrol). The aim of this paper is to combine the existing in vitro and in vivo models and clinical research results to summarize the efficacy and mechanism of natural drugs and targeted drugs in SLE for the reference and consideration of researchers.
Keywords: antibody drug; immune system; natural products; systemic lupus erythematosus; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Liu, Zang, Liang, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging B-Cell Therapies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021 Jan 14;17:39-54. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S252592. eCollection 2021. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021. PMID: 33488082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy of novel B cell biologics as the future of SLE treatment: a review.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Nov;13(11):1094-101. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.020. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 25149393 Review.
-
Systematic review, and meta-analysis of steroid-sparing effect, of biologic agents in randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials for systemic lupus erythematosus.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Oct;48(2):221-239. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018. PMID: 29426575
-
B cell depletion and inhibition in systemic lupus erythematosus.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Jan;19(1):55-70. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2145281. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36342225 Review.
-
The safety and efficacy of biologic agents in treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: A network meta-analysis.Pak J Med Sci. 2019 Nov-Dec;35(6):1680-1686. doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.6.771. Pak J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31777515 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Antioxidant Transcription Factor Nrf2 and Its Activating Compounds in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;13(10):1224. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101224. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early human migration determines the risk of being attacked by wolves: ethnic gene diversity on the development of systemic lupus erythematosus.J Rheum Dis. 2024 Oct 1;31(4):200-211. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0051. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 39355544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal B. B., Harikumar K. B. (2009). Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 41, 40–59. 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.06.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous