Drug Therapy Problems and Associated Factors Among Hypertensive Patients in North Wollo Public Hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia: Institutional-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 37492163
- PMCID: PMC10364825
- DOI: 10.2147/IBPC.S416585
Drug Therapy Problems and Associated Factors Among Hypertensive Patients in North Wollo Public Hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia: Institutional-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Drug therapy problems (DTPs) are common in people with hypertension and may threaten the effective management of the disease. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence and predictors for DTPs in hypertensive people in North Wollo public hospitals.
Methods: On patients with hypertension, a cross-sectional study based in a health institution was carried out using an interviewer-administered structured questionnaire and medical record review from 6 November 2022 to 18 January 2023. All hypertensive patients, ages 18 and older, who underwent regular follow-ups for at least 12 months were included in the study using a simple random sampling method. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to establish the association between independent variables and the occurrence of DTPs. Unnecessary drug therapy, the need for additional drug therapy, ineffective drugs, dosage too low, dosage too high, adverse drug reactions, and noncompliance were the outcome variables.
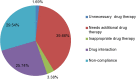
Results: The study included 376 hypertensive patients. Of the total participants, 258 (68.6%) were female. The mean number of drug therapy problems per patient was 1.55 ± 0.307, with 298 participants (79.3%) reporting having at least one such problem. This study found that the need for additional drug therapy was the most prevalent problem (149, 39.66%). Polypharmacy (AOR = 2.487, 95% CI = 1.375-4.499, p = 0.003), presence of comorbidity (AOR = 1.886, 95% CI = 1.035-3.439, p = 0.038), and uncontrolled BP (AOR = 2.961, 95% CI = 1.669-5.254, p = <0.001) predicts the development of drug therapy problems.
Conclusion: Patients with hypertension who are on follow-up experience drug therapy problems frequently. Promoting the involvement of clinical pharmacists in designing, implementing, and monitoring therapeutic plans is recommended to decrease the occurrence of drug therapy problems.
Keywords: Ethiopia; drug therapy problems; hypertension; hypertensive; public hospitals.
© 2023 Baye et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and factors associated with drug therapy problems among hypertensive patients at hypertension clinic of Mbarara Regional Referral Hospital, Uganda: a |cross-sectional study.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Jan-Dec;17:17539447231160319. doi: 10.1177/17539447231160319. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37036058 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure self-monitoring practice and associated factors among adult hypertensive patients on follow-up at South Wollo Zone Public Hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia.Open Heart. 2023 Mar;10(1):e002274. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2023-002274. Open Heart. 2023. PMID: 36958769 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapy problems and associated factors among type 2 adult diabetic patients on follow up at Mizan-Tepi University Teaching Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 4;18(8):e0288093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288093. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37540642 Free PMC article.
-
Drug therapy problems and contributing factors in the management of heart failure patients in Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 23;13(10):e0206120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206120. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30352096 Free PMC article.
-
Drug therapy problems, medication adherence and treatment satisfaction among diabetic patients on follow-up care at Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 1;14(10):e0222985. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222985. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31574113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dymek J, Pelka P, Polak W, Golda A, Skowron A. Drug related problems among ambulatory patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension. Int J Clin Pharm. 2016;38:1021.
-
- Chiazor IE, Oparah AC. Assessment of hypertension care in a Nigerian Hospital. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(1):137–145. doi:10.4314/tjpr.v11i1.18 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources