CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES AND QUALITY OF LIFE
- PMID: 37492372
- PMCID: PMC10364111
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.03.18
CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES AND QUALITY OF LIFE
Abstract
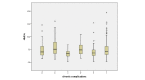
The course of diabetes is marked by the development of chronic complications that, in addition to affecting health, also affect the quality of life of patients. The purpose of this study was to compare the quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes based on their chronic complications. The study, which was conducted from March 2019 until March 2020, included 382 diabetic patients, specific data from medical records, and the application of the World Health Organization Quality of Life-Brief questionnaire. There were more men than women included in the study, with the majority of respondents belonging to the age group of 61 to 70 years. In the quality-of-life assessment, the mean value of physical functioning was 57.14 (42.86-71.43), psychological functioning was 66.67 (54.17-79.17), social functioning 66.67 (50.00-75.00), and environmental functioning was 68.75 (50.00-75.00). The domains of social functioning were lowest in patients with diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy, while the physical functioning domains were rated lowest in patients with diabetic nephropathy, diabetic foot ulcer, and multiple chronic complications. All domains were rated lowest by patients with multiple complications and highest by those without any complications. In conclusion, differences in the assessment of quality of life of diabetic patients depend on the type of chronic complication.
Keywords: , diabetic foot ulcer; nephropathy; neuropathy; quality of life; retinopathy; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Eger RJ, Maridal JH. A statistical meta-analysis of the wellbeing literature. Int J Wellbeing. 2015. June 21;5(2) 10.5502/ijw.v5i2.4 - DOI
-
- Stevanović R, Capak K, Benjak T. CROATIAN HEALTH STATISTICS YEARBOOK 2019. Croatian Institute of Public Health; 2020 Sep. Cited 2021 Jun 25. Available from: https://www.hzjz.hr/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Ljetopis_Yerabook_2019.pdf
-
- Poljičanin T. Uloga praćenja dijabetičkih bolesnika pomoću registra CroDiab u prevenciji komplikacija. 2010.
-
- Mehović S, Janković S, Tafi Z. Quality of Life Assessment in Type 2 Diabetes Patients With Cardiovascular and/or Diabetic Complications. Southeastern European Medical Journal: SEEMEDJ. 2021;5(1):75–88.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical