Case report: Basivertebral nerve block during vertebral augmentation: an alternative approach to intraprocedural pain management
- PMID: 37492392
- PMCID: PMC10365104
- DOI: 10.3389/fradi.2023.1179023
Case report: Basivertebral nerve block during vertebral augmentation: an alternative approach to intraprocedural pain management
Abstract
Osteoporotic compression fractures can be treated with vertebral augmentation. Since intraprocedural pain is common during vertebral body endplate manipulation, these procedures are often performed with conscious sedation or general anesthesia. Research has shown that vertebral endplates are innervated by the basivertebral nerve (BVN), which has been successfully targeted via radiofrequency ablation to treat chronic vertebrogenic lower back pain. With this physiology in mind, we evaluated if temporary BVN block would provide sufficient analgesia so that patients could forego sedation during percutaneous vertebral augmentation. Ten patients with single-level vertebral compression fractures were selected. Prior to balloon augmentation, temporary intraosseous BVN block was achieved using 2% lidocaine injection. All ten patients successfully completed their procedure without intraprocedural sedative or narcotic medications, and without significant deviation from baseline vital signs. Temporary BVN block can be used as intraprocedural anesthesia in select patients who may be poor candidates for general anesthesia or conscious sedation.
Keywords: anesthesia; kyphoplasty; nerve block; pain; vertebral augmentation; vertebroplasty.
© 2023 Santoro, Kulkarni, Dhillon and Lien.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
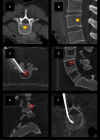
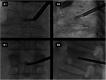
Similar articles
-
A prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain.Spine J. 2019 Oct;19(10):1620-1632. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.05.598. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 31229663 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 24-Month treatment arm results.N Am Spine Soc J. 2021 Oct 26;8:100089. doi: 10.1016/j.xnsj.2021.100089. eCollection 2021 Dec. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021. PMID: 35141653 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-osseous basivertebral nerve radiofrequency ablation (BVA) for the treatment of vertebrogenic chronic low back pain.Neuroradiology. 2021 May;63(5):809-815. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02577-8. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Neuroradiology. 2021. PMID: 33051706 Clinical Trial.
-
Best Practice Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Vertebrogenic Pain with Basivertebral Nerve Ablation from the American Society of Pain and Neuroscience.J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 14;15:2801-2819. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S378544. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36128549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventional Procedures for Vertebral Diseases: Spinal Tumor Ablation, Vertebral Augmentation, and Basivertebral Nerve Ablation-A Scoping Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Nov 15;9(11):1554. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9111554. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beall DP, Chambers MR, Thomas S, Amburgy J, Webb JR, Goodman BS, et al. Prospective and multicenter evaluation of outcomes for quality of life and activities of daily living for balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: the EVOLVE trial. Neurosurgery. (2019) 84(1):169–78. 10.1093/neuros/nyy017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

