Design, synthesis, in silico studies, and biological evaluation of novel pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives as potential anti-proliferative agents, VEGFR-2 inhibitors and apoptotic inducers
- PMID: 37492514
- PMCID: PMC10363774
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra04182d
Design, synthesis, in silico studies, and biological evaluation of novel pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives as potential anti-proliferative agents, VEGFR-2 inhibitors and apoptotic inducers
Abstract
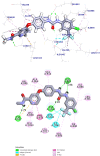
A novel series of pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives bearing benzylidene and hydrazone moieties with different linkers (spacers) were designed and synthesized as possible inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2). The newly synthesized compounds were evaluated in vitro for their cytotoxic activities against two human cancer cell lines namely colon cancer (HCT-116) and breast cancer (MCF-7) using sorafenib as a standard anticancer drug. Compounds 9d, 11e, 12b, and 12d showed higher cytotoxic activities than sorafenib with IC50 values ranging from 1.14 to 10.33 μM. In particular, compound 11e exhibited excellent activities against HCT-116 and MCF-7 with IC50 values of 1.14 and 1.54 μM, respectively. Moreover, compound 11e exhibited about 47.32-fold cytotoxic activity against normal human fibroblast (WI-38) cells, lower than the cytotoxicity against the cancer cells. Compounds 11e and 12b were the most potent VEGFR-2 inhibitors with IC50 values of 0.61 and 0.53 μM, respectively, compared to sorafenib. Bedsides, compound 11e arrested the HCT-116 cell growth at S and sub-G1 phases, induced a significant increase in the apoptotic cells, and caused remarkable decrease in the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and caspase-3. Finally, the binding patterns of the target derivatives were investigated through the docking study against the proposed molecular target (VEGFR-2, PDB ID 1YWN). The results of molecular docking studies showed similar binding modes to sorafenib against VEGFR-2. In addition, molecular dynamic simulations revealed the stability of compound 11e in the active site for 100 ns.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by the authors and there is no any conflict of interest.
Figures

























References
-
- Ganapathy V. Thangaraju M. Prasad P. D. Nutrient transporters in cancer: relevance to Warburg hypothesis and beyond. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2009;121(1):29–40. - PubMed
-
- Varmus H. The new era in cancer research. Science. 2006;312(5777):1162–1165. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z. Shi X.-H. Wang J. Zhou T. Xu Y.-Z. Huang T.-T. et al., Synthesis, structure–activity relationships and preliminary antitumor evaluation of benzothiazole-2-thiol derivatives as novel apoptosis inducers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011;21(4):1097–1101. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R. L. Miller K. D. Jemal A. Cancer statistics. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Saleh N. M. Abdel-Rahman A. A. H. Omar A. M. Khalifa M. M. El-Adl K. Pyridine-derived VEGFR-2 inhibitors: rational design, synthesis, anticancer evaluations, in silico ADMET profile, and molecular docking. Arch. Pharm. 2021;354(8):2100085. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

