Identifying novel candidate compounds for therapeutic strategies in retinopathy of prematurity via computational drug-gene association analysis
- PMID: 37492605
- PMCID: PMC10365641
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1151239
Identifying novel candidate compounds for therapeutic strategies in retinopathy of prematurity via computational drug-gene association analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is the leading cause of preventable childhood blindness worldwide. Although interventions such as anti-VEGF and laser have high success rates in treating severe ROP, current treatment and preventative strategies still have their limitations. Thus, we aim to identify drugs and chemicals for ROP with comprehensive safety profiles and tolerability using a computational bioinformatics approach.
Methods: We generated a list of genes associated with ROP to date by querying PubMed Gene which draws from animal models, human studies, and genomic studies in the NCBI database. Gene enrichment analysis was performed on the ROP gene list with the ToppGene program which draws from multiple drug-gene interaction databases to predict compounds with significant associations to the ROP gene list. Compounds with significant toxicities or without known clinical indications were filtered out from the final drug list.
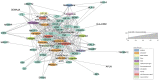
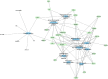
Results: The NCBI query identified 47 ROP genes with pharmacologic annotations present in ToppGene. Enrichment analysis revealed multiple drugs and chemical compounds related to the ROP gene list. The top ten most significant compounds associated with ROP include ascorbic acid, simvastatin, acetylcysteine, niacin, castor oil, penicillamine, curcumin, losartan, capsaicin, and metformin. Antioxidants, NSAIDs, antihypertensives, and anti-diabetics are the most common top drug classes derived from this analysis, and many of these compounds have potential to be readily repurposed for ROP as new prevention and treatment strategies.
Conclusion: This bioinformatics analysis creates an unbiased approach for drug discovery by identifying compounds associated to the known genes and pathways of ROP. While predictions from bioinformatic studies require preclinical/clinical studies to validate their results, this technique could certainly guide future investigations for pathologies like ROP.
Keywords: bioinformatics; bioinformatics & computational biology; drug discovery; network medicine; retina; retinopathy of prematurity.
© 2023 Xie, Hilkert Rodriguez, Xie, D'Souza, Reem, Sulakhe and Skondra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using Advanced Bioinformatics Tools to Identify Novel Therapeutic Candidates for Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 May 1;12(5):19. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.5.19. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37191619 Free PMC article.
-
Using Computational Drug-Gene Analysis to Identify Novel Therapeutic Candidates for Retinal Neuroprotection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 21;23(20):12648. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012648. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293505 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-VEGF therapy in the management of retinopathy of prematurity: what we learn from representative animal models of oxygen-induced retinopathy.Eye Brain. 2016 May 20;8:81-90. doi: 10.2147/EB.S94449. eCollection 2016. Eye Brain. 2016. PMID: 28539803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Advanced Bioinformatics Tools to Identify Novel Therapeutic Candidates for Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Aug 1;11(8):10. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.8.10. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35972434 Free PMC article.
-
Retinopathy of Prematurity: Therapeutic Strategies Based on Pathophysiology.Neonatology. 2016;109(4):369-76. doi: 10.1159/000444901. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Neonatology. 2016. PMID: 27251645 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

