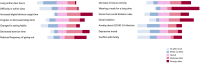The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic era on children with primary headache: a questionnaire survey study and literature review
- PMID: 37492607
- PMCID: PMC10364439
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1179979
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic era on children with primary headache: a questionnaire survey study and literature review
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has resulted in individual isolation and secondary problems, especially in children. Research on the effect of the social isolation on children with primary headache is limited. This study aimed at exploring the effects of environmental changes caused by COVID-19 on headache in children.
Methods: This cross-sectional survey study enrolled school-aged children (age, 8-16 years) with headache who were able to complete the questionnaire from a Pediatric Headache Clinic between January 2021 and December 2022. Headache diaries for all patients were in their medical records and two questionnaire responses were requested at a 3-month interval. The questionnaires included headache type, frequency, previous medical conditions, family history, Pediatric Migraine Disability Assessment scores (PedMIDAS) scores, changes in daily life after COVID-19, and factors that aggravated headaches associated with social distancing.
Results: We identified 35 patients who were diagnosed with primary headache and continued to visit our outpatient clinic for at least 3 months. Among them, 33 (15 males and 18 females) patients responded to the first survey. The average age (±SD) of patients was 12.5 ± 1.9 years. PedMIDAS scores were not affected by the COVID-19 infection history. Prolonged use of masks and increased use of digital devices were reported as the most common factors that aggravated headache during the pandemic era.
Conclusion: COVID-19 did not affect in worsening primary headache in children. However, the pandemic can introduce various changes in daily life, which in turn can affect the management of headache. By gathering feedback regarding the thoughts of the patients on the impact of the current pandemic environment, patient counseling on the precautions and management can be conducted in advance in the case of repeated lockdown in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; children; migraine; pandemic; primary headache.
© 2023 Yoon, Kim and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triggers and clinical changes of childhood primary headache characteristics during COVID-19 pandemic lockdown.Acta Neurol Belg. 2023 Feb;123(1):215-220. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-02150-5. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Acta Neurol Belg. 2023. PMID: 36478546 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on migraine in Japan: a multicentre cross-sectional study.J Headache Pain. 2021 Jun 7;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01263-1. J Headache Pain. 2021. PMID: 34098873 Free PMC article.
-
Essential headaches in developmental age: What is changed before, during and after the lockdown for COVID-19 pandemic. Clinical study.Front Pediatr. 2023 Apr 25;11:1166984. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1166984. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37181428 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence, impact, and treatment of migraine and severe headaches in the United States: a review of statistics from national surveillance studies.Headache. 2013 Mar;53(3):427-36. doi: 10.1111/head.12074. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Headache. 2013. PMID: 23470015 Review.
-
Headache attributed to SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination and the impact on primary headache disorders of the COVID-19 pandemic: A comprehensive review.Cephalalgia. 2023 Jan;43(1):3331024221131337. doi: 10.1177/03331024221131337. Cephalalgia. 2023. PMID: 36606562 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of digital device use on the risk of migraine: a univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1462414. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1462414. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39539656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dal-Pai J, Dos Santos MP, Donida NDS, Cesarino MR, de Oliveira V, Nunes ML. Health consequences and daily life modifications in children and adolescents with epilepsy during the COVID-19 pandemic - a systematic review: running title: COVID-19 pandemic in children/adolescents with epilepsy. Seizure. (2023) 108:102–15. 10.1016/j.seizure.2023.04.017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources