LRP1B suppresses HCC progression through the NCSTN/PI3K/AKT signaling axis and affects doxorubicin resistance
- PMID: 37492741
- PMCID: PMC10363646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.021
LRP1B suppresses HCC progression through the NCSTN/PI3K/AKT signaling axis and affects doxorubicin resistance
Abstract
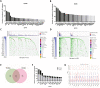
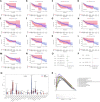
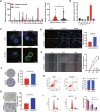
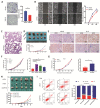
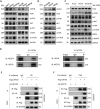
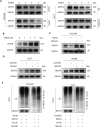
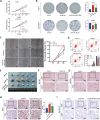
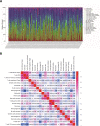
Accumulating evidence supports the association of somatic mutations with tumor occurrence and development. We aimed to identify somatic mutations with important implications in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and explore their possible mechanisms. The gene mutation profiles of HCC patients were assessed, and the tumor mutation burden was calculated. Gene mutations closely associated with tumor mutation burden and patient overall survival were identified. In vivo and in vitro experiments were performed to verify the effects of putative genes on proliferation, invasion, drug resistance, and other malignant biological behaviors of tumor cells. Fourteen genes with a high mutation frequency were identified. The mutation status of 12 of these genes was closely related to the mutation burden. Among these 12 genes, LRP1B mutation was closely associated with patient prognosis. Nine genes were associated with immune cell infiltration. The results of in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that the knockdown of LRP1B promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration and enhances the resistance of tumor cells to liposomal doxorubicin. LRP1B could directly bind to NCSTN and affect its protein expression level, thereby regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Our mutational analysis revealed complex and orchestrated liposomal alterations linked to doxorubicin resistance that may also render cancers less susceptible to immunotherapy and also provides new treatment alternatives.
Keywords: Doxorubicin; Hepatocellular carcinoma; LRP1B; PI3K/AKT pathway; Tumor mutation burden.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

