ChatDoctor: A Medical Chat Model Fine-Tuned on a Large Language Model Meta-AI (LLaMA) Using Medical Domain Knowledge
- PMID: 37492832
- PMCID: PMC10364849
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.40895
ChatDoctor: A Medical Chat Model Fine-Tuned on a Large Language Model Meta-AI (LLaMA) Using Medical Domain Knowledge
Abstract
Objective The primary aim of this research was to address the limitations observed in the medical knowledge of prevalent large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, by creating a specialized language model with enhanced accuracy in medical advice. Methods We achieved this by adapting and refining the large language model meta-AI (LLaMA) using a large dataset of 100,000 patient-doctor dialogues sourced from a widely used online medical consultation platform. These conversations were cleaned and anonymized to respect privacy concerns. In addition to the model refinement, we incorporated a self-directed information retrieval mechanism, allowing the model to access and utilize real-time information from online sources like Wikipedia and data from curated offline medical databases. Results The fine-tuning of the model with real-world patient-doctor interactions significantly improved the model's ability to understand patient needs and provide informed advice. By equipping the model with self-directed information retrieval from reliable online and offline sources, we observed substantial improvements in the accuracy of its responses. Conclusion Our proposed ChatDoctor, represents a significant advancement in medical LLMs, demonstrating a significant improvement in understanding patient inquiries and providing accurate advice. Given the high stakes and low error tolerance in the medical field, such enhancements in providing accurate and reliable information are not only beneficial but essential.
Keywords: ai chatbot; chat gpt; gpt; large language model; llama.
Copyright © 2023, Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
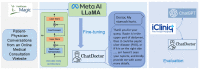











References
-
- Long Ouyang, Jeff Wu, Xu Jiang, et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv preprint. [ Apr; 2023 ]. 2022. http://arXiv:2203.02155 p. 0.http://arXiv:2203.02155
-
- Yizhong Wang, Yeganeh Kordi, Swaroop Mishra, Alisa Liu, Noah A. Smith, Daniel Khashabi, Hannaneh Hajishirzi. Self-instruct: aligning language model with self generated instructions. arXiv preprint. [ Dec; 2022 ]. 2022. http://arXiv:2212.10560 p. 0.http://arXiv:2212.10560
-
- How does chatgpt perform on the united states medical licensing examination? the implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. Aidan Gilson, Conrad W Safranek, Thomas Huang, et al. https://mededu.jmir.org/2023/1/e45312/ JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9:45312–42023. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Means: a medical question-answering system combining NLP techniques and semantic web technologies. Abacha AB, Zweigenbaum P. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306457315000515 Inf Process Manag. 2015;51:570–594.
-
- Rohan Taori, Ishaan Gulrajani, Tianyi Zhang, et al. Stanford alpaca: an instruction-following llama model. [ Apr; 2023 ]. 2023. https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
