Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp3)-C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Alkyl Halides with Alkyl Tosylates
- PMID: 37494617
- PMCID: PMC10416217
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c07313
Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp3)-C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Alkyl Halides with Alkyl Tosylates
Abstract
Formation of new C(sp3)-C(sp3) bonds is a powerful synthetic tool to increase molecular diversity, which is highly sought after in medicinal chemistry. Traditional generation of carbon nucleophiles and more modern cross-electrophile-coupling methods typically lack sufficient selectivity when cross-coupling of analogous C(sp3)-containing reactants is attempted. Herein, we present a nickel-catalyzed, electrochemically driven method for the coupling of alkyl bromides with alkyl tosylates. Selective cross-coupling transformations were achieved even between C(sp3)-secondary bromides and tosylates. Key to achieve high selectivity was the combination of the tosylates with sodium bromide as the supporting electrolyte, gradually generating small amounts of the more reactive bromide by substitution and ensuring that one of the reaction partners in the nickel-catalyzed electroreductive process is maintained in excess during a large part of the process. The method has been demonstrated for a wide range of substrates (>30 compounds) in moderate to good yields. Further expanding the scope of electroorganic synthesis to C(sp3)-C(sp3) cross-coupling reactions is anticipated to facilitate the switch to green organic synthesis and encourage future innovative electrochemical transformations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

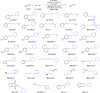
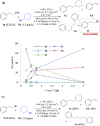
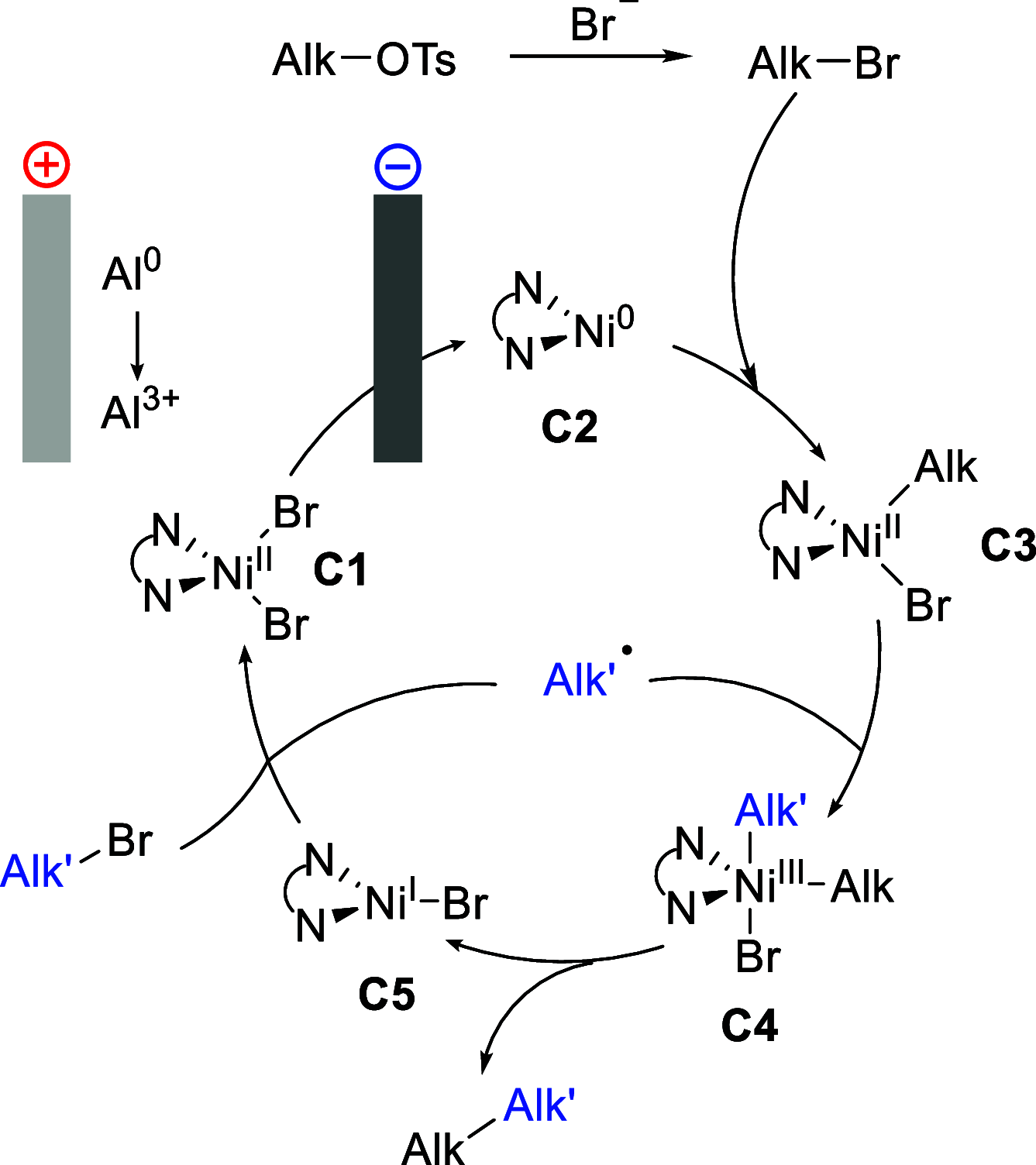
References
-
- Cárdenas D. J. Towards Efficient and Wide-Scope Metal Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3018–3020. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991018)38:20<3018::AID-ANIE3018>3.0.CO;2-F. - DOI - PubMed
- Luh T.-Y.; Leung M.-K.; Wong K.-T. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Activation of Aliphatic C-X Bonds in Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3187–3204. 10.1021/cr990272o. - DOI - PubMed
- Netherton M. R.; Fu G. C. Nickel-Catalyzed Cross Couplings of Unactivated Alkyl Halides and Pseudohalides with Organometallic Compounds. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1525–1532. 10.1002/adsc.200404223. - DOI
-
- Yu X.; Yang T.; Wang S.; Xu H.; Gong H. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Cross-Coupling of Unactivated Alkyl Halides. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2138–2141. 10.1021/ol200617f. - DOI - PubMed
- Xu H.; Zhao C.; Qian Q.; Deng W.; Gong H. Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of unactivated alkyl halides using bis(pinacolato)diboron as reductant. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4022–4029. 10.1039/c3sc51098k. - DOI
-
- Komeyama K.; Michiyuki T.; Osaka I. Nickel/Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp3)-C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Alkyl Halides with Alkyl Tosylates. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9285–9291. 10.1021/acscatal.9b03352. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

