Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis to replace in-feed antibiotics of broiler chickens under necrotic enteritis-challenged experiments: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37494807
- PMCID: PMC10393822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102923
Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis to replace in-feed antibiotics of broiler chickens under necrotic enteritis-challenged experiments: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
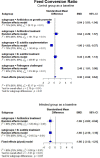
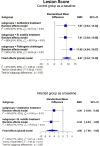
Necrotic enteritis (NE) and coccidiosis are among the most prevalent infectious diseases in broiler chickens, contributing to large profitability losses. Bacillus subtilis is a promising direct-fed probiotic to counter various pathogens infection in broiler chickens. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to investigate the effects of B. subtilis on broiler chickens performance. A total of 28 studies were selected according to a PRISMA checklist. Random-effect model and mixed-effect model of meta-analysis were fitted to estimate the overall effects of B. subtilis (BS) treatment compared to either the control group (CON) or NE-infected group (NEinf) as a baseline. Hedges' g effect size and its variance were used as estimators of standardized mean difference (SMD) calculation where the results were presented at a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of the SMD. Overall, NEinf broiler chickens depressed (P < 0.01) body weight (BW), average daily gain (ADG), and feed intake, and elevated (P < 0.01) feed conversion ratio (FCR). Treatment with BS improved ADG and final BW of NEinf with no difference (P = 0.15) between BS and antibiotics (AB), indicating that they had comparable efficacy to treat NE in broiler chickens. BS supplemented to uninfected CON (BSS) improved (P < 0.01) final BW, ADG, and FCR. Compared to CON, BS, and AB failed to recover the FCR but these treatments decreased (P < 0.01) FCR when compared to the NEinf group with similar efficacy (P = 0.97). As expected, NEinf birds had a higher mortality rate (P < 0.01) and higher lesion score (P < 0.01) compared to CON, and treatment using AB and BS successfully decreased (P < 0.01) the mortality rate and lesion score. Compared to BS, AB was more effective to lower (P = 0.01) mortality rate, but comparable (P = 0.65) to minimize lesion score. To conclude, B. subtilis could be an effective natural additive to replace in-feed antibiotics in broiler chickens challenged with C. perfringens. However, the efficacy to reduce mortality rate was better with antibiotics treatment.
Keywords: Clostridium perfringens; Eimeria; alternative antibiotics; antimicrobial resistance; probiotics.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Elbestawy A.R., El-Shall N.A., Saad A.M., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., Khafaga A.F., Taha A.E., AbuQamar S.F., El-Tarabily K.A. Necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens: disease characteristics and prevention using organic antibiotic alternatives – a comprehensive review. Poult. Sci. 2022,;101 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abudabos A.M., Alyemni A.H., AlMarshad M.B.A. Bacillus subtilis PB6 based-probiotic (CloSTATTM) improves intestinal morphological and microbiological status of broiler chickens under clostridium perfringens challenge. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2013;15:978–982.
-
- Abudabos A.M., Alyemni A.H., Dafalla Y.M., Al-Owaimer A.N. Effect of organic acid blend and bacillus subtilis on growth, blood metabolites and antioxidant status in finishing broilers challenged with clostridium perfringens. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2017;27:1101–1107.
-
- Adhikari P., Kiess A., Adhikari R., Jha R. An approach to alternative strategies to control avian coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020;29:515–534.
-
- Agunos A., Gow S.P., Leger D.F., Carson C.A., Deckert A.E., Bosman A.L., Loest D., Irwin R.J., Reid-Smith R.J. Antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance indicators – integration of farm-level surveillance data from broiler chickens and turkeys in British Columbia, Canada. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019,;6:1–16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

